Каталог оснастка Dormer Pramet 2016 - страница 261
Навигация
- DIN 69871
- 69871-CC-OZ
- 69871-CC-ER
- 69871-CC-ER
- 69871-CC-ER
- 69871-CCM-ER
- 69871-CC-HKS
- 69871-W
- 69871-W
- 69871-W
- 69871-W-C
- 69871-W-C
- 69871-MT
- 69871-MTS
- 69871-RED-ISO
- 69871-FMH2
- 69871-FMH2
- 69871-FMH1
- 69871-FMH1
- 69871-FMH4
- 69871-DC
- 69871-QTCC
- 69871-QTCW
- 69871-HC
- 69871-HC
- 69871-SC
- 69871-SC
- 69871-SC
- 69871-SC
- 69871-SC-C
- 69871-IHA
- 69871-BLANKS
- 69871-TA
- ISO 60
- ISO-60-FMH1
- ISO-60-MT
- ISO-60-MTS
- ISO-60-RED-ISO
- MAS 403 BT
- BT-CC-OZ
- BT-CC-ER
- BT-CC-ER
- BT-CC-ER
- BT-CCM-ER
- BT-CC-HKS
- BT-W
- BT-W
- BT-W
- BT-W-C
- BT-W-C
- BT-MT
- BT-MTS
- BT-RED-ISO
- BT-FMH2
- BT-FMH2
- BT-FMH1
- BT-FMH1
- BT-FMH4
- BT-DC
- BT-QTCC
- BT-QTCW
- BT-HC
- BT-HC
- BT-SC
- BT-SC
- BT-SC
- BT-SC-C
- BT-IHA
- Bez názvu
- BT-TA
- DIN 2080
- 2080-CC-OZ
- 2080-CC-ER
- 2080-W
- 2080-W
- 2080-MT
- 2080-MTS
- 2080-RED-ISO
- 2080-FMH2
- 2080-FMH1
- 2080-DC
- 2080-QTCC
- 2080-BLANKS
- HSK-A
- HSK-A-CC-OZ
- HSK-A-CC-ER
- HSK-A-CCM-ER
- HSK-A-CC-HKS
- HSK-A-W
- HSK-A-W
- HSK-A-W-C
- HSK-A-FMH2
- HSK-A-FMH1
- HSK-A-FMH1
- HSK-A-FMH4
- HSK-A-MT
- HSK-A-MTS
- HSK-A-QTCC
- HSK-A-QTCW
- HSK-A-DC
- HSK-A-HC
- HSK-A-HC
- HSK-A-HC
- HSK-A-SC
- HSK-A-SC
- HSK-A-SC
- HSK-A-SC
- HSK-A-SC-C
- HSK-A-SC-C
- HSK-A-IHA
- HSK-A-BLANKS
- HSK-A-TA
- VDI
- VDI-B1
- VDI-B2
- VDI-B3
- VDI-B4
- VDI-B5
- VDI-B6
- VDI-B7
- VDI-B8
- VDI-C1
- VDI-C2
- VDI-C3
- VDI-C4
- VDI-D1
- VDI-D2
- VDI-AR
- VDI-AL
- VDI-E1
- VDI-E2
- VDI-E3
- VDI-E4
- VDI-F1
- VDI-HC
- VDI-Z2-S
- VDI-Z2-P
- VDI-DC
- VDI-DC-C
- VDI-QTCC
- VDI-QTCW
- VDI-A1
- VDI-A2
- VDI-TA
- MORSE
- MORSE-CC-ER
- MORSE-FMH2
- MORSE-QTCC
- MORSE-RED-MT
- MORSE-DC
- ADAPTORS / ADAPTÉRY ПЕРЕХОДНИК / 转接套
- AC-CC-ER
- ACF-CC-ER
- ACF-CC-ER-HX
- ACF-CCM-ER
- ACF-CCM-ER
- ACF-CCM-ER-D
- AC-HC
- AC-SC
- AW-DC
- AW-QTCC
- AW-QTCW
- AW-RED-W
- ACCESSORIES / PŘÍSLUŠENSTVÍ АКСЕССУАРЫ / 附件
- PS-69872
- PS-7388
- PS-BT
- PS-BT-C-S
- PS-2080-C
- OZ-C
- OZ-C-P
- OZ-C-SET-WP
- OZ-C-SET-WB
- OZ-C-SET-P-WP
- OZ-C-SET-P-WB
- ER-C
- ER-C-P
- ER-C-S
- ER-C-SC4
- ER-T
- ER-T-SC4
- ER-C-SET-WP
- ER-C-SET-WB
- ER-C-SET-P-WP
- ER-C-SET-P-WB
- ER-C-SET-S-WP
- ER-C-SET-S-WB
- ER-C-SET-SC4-WP
- ER-C-SET-SC4-WB
- ER-T-SET-WP
- ER-T-SET-WB
- ER-T-SET-SC4-WP
- ER-T-SET-SC4-WB
- HC-C
- HC-C-S
- QTCW-1
- QTCW-2
- QTCW-3
- QTCC-1
- QTCC-2
- QTCC-3
- QTCR
- HKS-C
- HKS-C-S
- N-OZ
- N-OZ-SR
- SR-OZ
- N-ER-M
- N-ER
- N-ER-SR
- N-ER-SR-SN
- SR-ER
- K-HKS
- K-OZ
- K-ER
- K-ER-M
- K-FMH
- E-MORSE
- E-HKS
- S-FMH
- S-FMH-C
- S-W
- F-FMH2
- DR-FMH2
- DS-FMH4
- S-DS-FMH4
- CT-HSK-A
- K-CT-HSK-A
- VDI-RS-E2
- VDI-SHIMS
- VDI-NOZZ
- TW
- AB-A360
- AB-S90
- TECHNICAL PART
- Steep Taper
- Pull studs
- HSK (hollow taper shanks)
- HSK coolant tubes
- Effects of imbalance on machine spindles, toolholders and tools
- Hydraulic expansion chucks
- Operating and user instructions for hydraulic expansion chucks
- Torques for clamping end-mills in end mill holders DIN 6359
- Operating and user instructions for CNC-drill chucks
- Mounting instructions for ER-Collets per DIN STD 6499
- Mounting instruction for sealing discs
- Quick-change tapping chucks
- Instructions for tapping chucks
- Screw taps-shaft size
- Tool assignment for disc turrets
- High-performance milling chucks HKS-system
- Product codes description
- TECHNICKÁ ČÁST
- STRMÝ KUŽEL
- TAŽNÉ ČEPY
- HSK (duté kuželové stopky)
- TRUBICE PRO ŘEZNOU KAPALINU HSK
- ÚČINKY NEROVNOVÁHY NA VŘETENA, DRŽÁKY A NÁSTROJE
- ÚČINKY NEROVNOVÁHY NA VŘETENA, DRŽÁKY A NÁSTROJE
- HYDROUPÍNAČE
- NÁVOD K OBSLUZE PRO HYDROUPÍNAČE
- UTAHOVACÍ MOMENTY ŠROUBŮ PRO UPNUTÍ STOPKOVÝCH FRÉZ V DRŽÁCÍCH DIN 6359
- NÁVOD K OBSLUZE PRO NC VRTACÍ HLAVIČKY
- NÁVOD K MONTÁŽI PRO KLEŠTINOVÉ UPÍNAČE ER PODLE DIN STD 6499
- NÁVOD K MONTÁŽI PRO TĚSNICÍ KROUŽKY
- RYCHLOVÝMĚNNÉ KLEŠTINOVÉ UPÍNAČE PRO ZÁVITOVÁNÍ
- NÁVOD PRO RYCHLOVÝMĚNNÉ ZÁVITOVACÍ UPÍNAČE
- TABULKA ČTYŘHRANŮ STOPEK ZÁVITNÍKŮ
- ZNAČENÍ A ORIENTACE DRŽÁKŮ VDI V REVOLVEROVÝCH HLAVÁCH
- SYSTÉM HKS SE SILOVÝMI UPÍNACÍMI POUZDRY
- POPISY KÓDŮ VÝROBKŮ
- ТЕХНИЧЕСКАЯ ЧАСТЬ
- КОНУС SK
- ШТРЕВЕЛИ
- КОНУС HSK (от англ. hollow taper shanks – полый конус)
- КОНУС HSK (от англ. hollow taper shanks – полый конус)
- Патрубки для подачи СОЖ к оправкам HSK
- ЭФФЕКТ ДИСБАЛАНСА ШПИНДЕЛЯ СТАНКА,ОПРАВОК И РЕЖУЩЕГО ИНСТРУМЕНТА
- ЭФФЕКТ ДИСБАЛАНСА ШПИНДЕЛЯ СТАНКА,ОПРАВОК И РЕЖУЩЕГО ИНСТРУМЕНТА
- ГИДРАВЛИЧЕСКИЕ ПАТРОНЫ
- ИНСТРУКЦИЯ ПО ЭКСПЛУАТАЦИИ ГИДРАВЛИЧЕСКИХ ПАТРОНОВ
- МОМЕНТЫ ЗАТЯЖКИ КОНЦЕВЫХ ФРЕЗ В ОПРАВКАХ ПО DIN 6359
- Инструкции по эксплуатации сверлильных патронов для станков с ЧПУ
- ИНСТРУКЦИИ ПО УСТАНОВКЕ ЦАНГ ER ПО DIN STD 6499
- ИНСТРУКЦИЯ ПО УСТАНОВКЕ УПЛОТНИТЕЛЬНЫХ КОЛЕЦ
- БЫСТРОСМЕННЫЕ РЕЗЬБОНАРЕЗНЫЕ ПАТРОНЫ
- ИНСТРУКЦИЯ ДЛЯ РЕЗЬБОНАРЕЗНЫХ ПАТРОНОВ
- СООТВЕТСТВИЕ РАЗМЕРА РЕЗЬБЫ И РАЗМЕРА ХВОСТОВИКА МЕТЧИКА
- ПРИМЕНЕНИЕ ИНСТРУМЕНТА В ДИСКОВОЙ РЕВОЛЬВЕРНОЙ ГОЛОВКЕ
- ВЫСОКОПРОИЗВОДИТЕЛЬНЫЕ ФРЕЗЕНЫЕ ОПРАВКИ СИСТЕМЫ HKS
- СИСТЕМА ОБОЗНАЧЕНИЯ
- 技术部分
- 锥柄
- 拉钉
- HSK(中空锥形柄)
- HSK冷却液管
- 不平衡对机床主轴、刀架和刀具的影响
- 不平衡对机床主轴、刀架和刀具的影响
- 液压刀柄
- 液压刀柄操作和使用说明
- 侧固刀柄(DIN 6359)端面铣刀夹紧扭矩
- CNC钻卡头操作和使用说明
- ER夹头安装说明,依照DIN STD 6499
- 密封圈安装说明
- 快速更换式攻丝卡盘
- 攻丝卡盘说明
- 攻丝-轴尺寸
- 盘塔刀具分配
- 强力刀柄HKS系统
- 产品代码描述
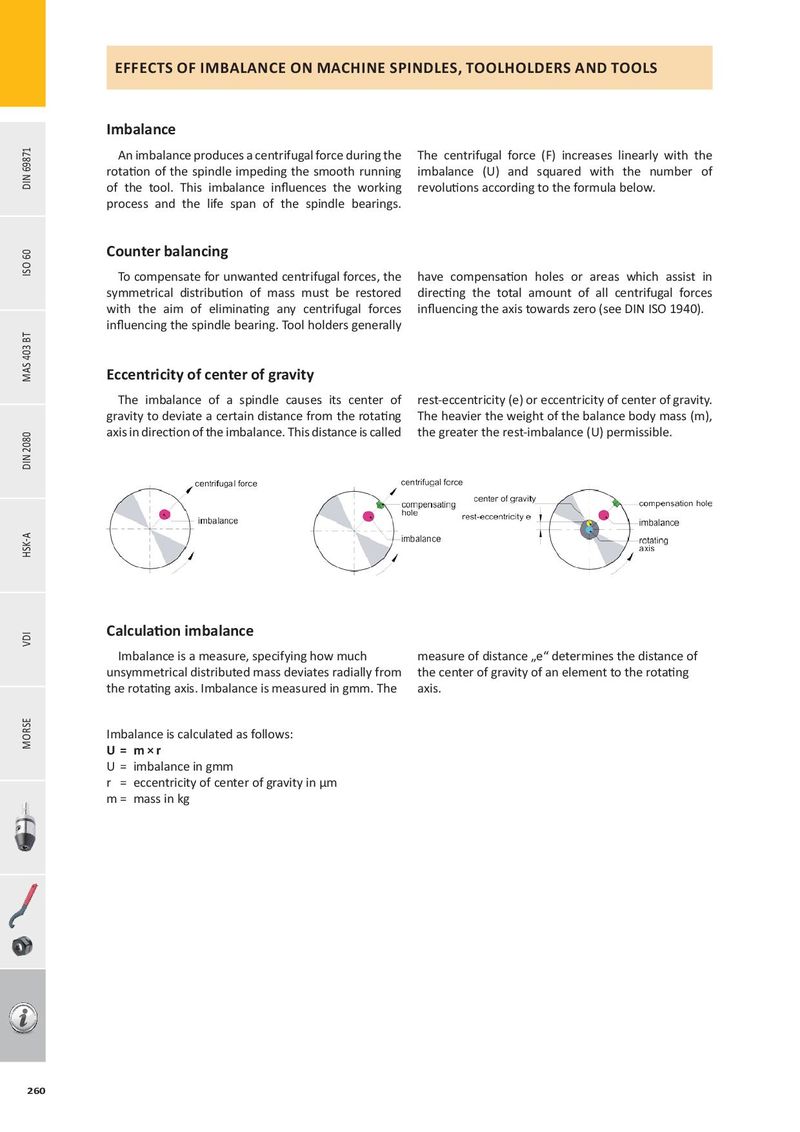
EFFECTS OF IMBALANCE ON MACHINE SPINDLES, TOOLHOLDERS AND TOOLS Imbalance An imbalance produces a centrifugal force during the The centrifugal force (F) increases linearly with the rotation of the spindle impeding the smooth running imbalance (U) and squared with the number of DIN 69871 of the tool. This imbalance influences the working revolutions according to the formula below. process and the life span of the spindle bearings. Counter balancing ISO 60 To compensate for unwanted centrifugal forces, the have compensation holes or areas which assist in symmetrical distribution of mass must be restored directing the total amount of all centrifugal forces with the aim of eliminating any centrifugal forces influencing the axis towards zero (see DIN ISO 1940). influencing the spindle bearing. Tool holders generally MA S 403 BT Eccentricity of center of gravity The imbalance of a spindle causes its center of rest-eccentricity (e) or eccentricity of center of gravity. gravity to deviate a certain distance from the rotating The heavier the weight of the balance body mass (m), axis in direction of the imbalance. This distance is called the greater the rest-imbalance (U) permissible. DIN 2080 HSK-A Calculation imbalance VDI Imbalance is a measure, specifying how much measure of distance „e“ determines the distance of unsymmetrical distributed mass deviates radially from the center of gravity of an element to the rotating the rotating axis. Imbalance is measured in gmm. The axis. Imbalance is calculated as follows: MORSE U = m × r U = imbalance in gmm r = eccentricity of center of gravity in μm m = mass in kg 260
 Общий каталог Dormer Pramet 2018
Общий каталог Dormer Pramet 2018 Каталог Dormer Pramet токарная обработка 2021 - 2022
Каталог Dormer Pramet токарная обработка 2021 - 2022 Брошюра Dormer Pramet новинки 2021
Брошюра Dormer Pramet новинки 2021 Каталог Dormer Pramet обработка резьбы 2021 - 2022
Каталог Dormer Pramet обработка резьбы 2021 - 2022 Каталог Dormer Pramet фрезерование 2021 - 2022
Каталог Dormer Pramet фрезерование 2021 - 2022