Техническая информация Sumitomo - страница 8
Навигация
 Каталог Sumitomo пластины с алмазными вставками Sumidia
Каталог Sumitomo пластины с алмазными вставками Sumidia Общий каталог Sumitomo 2019 - 2020
Общий каталог Sumitomo 2019 - 2020 Каталог Sumitomo токарные резцы (державки) для наружного точения
Каталог Sumitomo токарные резцы (державки) для наружного точения Каталог Sumitomo твердосплавные пластины
Каталог Sumitomo твердосплавные пластины Каталог Sumitomo фрезы со сменными пластинами
Каталог Sumitomo фрезы со сменными пластинами Каталог Sumitomo пластины с режущей кромкой-моноалмаз Sumicristal
Каталог Sumitomo пластины с режущей кромкой-моноалмаз Sumicristal 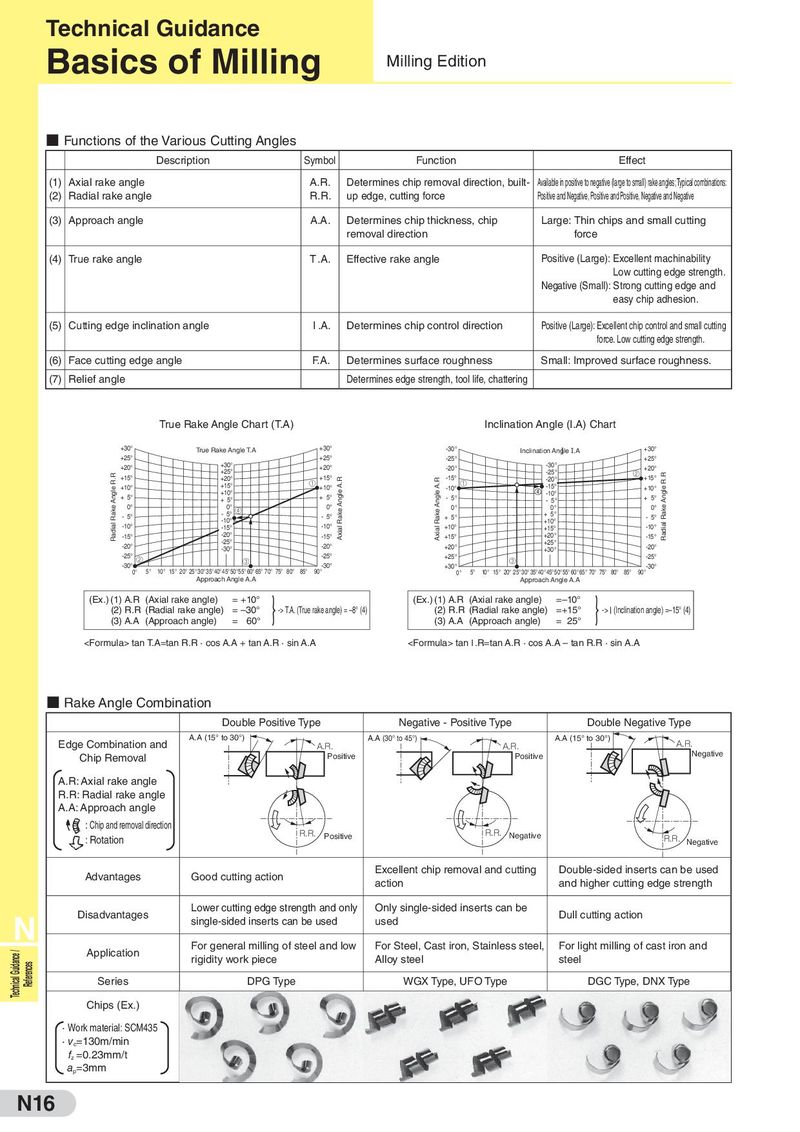
Technical Guidance
Basics of Milling Milling Edition
■ Functions of the Various Cutting Angles
Description Symbol Function Effect
(1) Axial rake angle A.R. Determines chip removal direction, built- Available in positive to negative (large to small) rake angles; Typical combinations:
(2) Radial rake angle R.R. up edge, cutting force Positive and Negative, Positive and Positive, Negative and Negative
(3) Approach angle A.A. Determines chip thickness, chip Large: Thin chips and small cutting
removal direction force
(4) True rake angle T .A. Effective rake angle Positive (Large): Excellent machinability
Low cutting edge strength.
Negative (Small): Strong cutting edge and
easy chip adhesion.
(5) Cutting edge inclination angle I .A. Determines chip control direction Positive (Large): Excellent chip control and small cutting
force. Low cutting edge strength.
(6) Face cutting edge angle F.A. Determines surface roughness Small: Improved surface roughness.
(7) Relief angle Determines edge strength, tool life, chattering
True Rake Angle Chart (T.A) Inclination Angle (I.A) Chart
+30° True Rake Angle T.A +30° -30° Inclination Angle I.A +30°
+25° +25° -25° +25°
+20° +30° +20° -20° -30° +20°
Radial Rake Angle R.R +15° +25° +15° -25° ② Radial Rake Angle R.R
+20° ① Axial Rake Angle A.R Axial Rake Angle A.R -15° -20° +15°
-10° ①
+10° +15° +10° -15° +10°
+ 5° +10° + 5° - 5° -10° + 5°
+ 5° - 5°
0° 0° ④ 0° 0° 0° 0°
- 5° - 5° - 5° + 5° + 5° - 5°
-10° -10° -10° +10°
-15° +10° +15° -10°
-15° -20° -15° +15° +20° -15°
-20° -25° -20° +20° +25° -20°
-30° +30°
-25° ② ③ -25° +25° ③ -25°
-30° 5° 10° 15° 20° 25° 30° 35°40°45°50°55° 60° 65° 70° 75° 80° 85° 90°-30° +30° -30°
0° 0° 5° 10° 15° 20° 25° 30° 35°40°45°50°55° 60° 65° 70° 75° 80° 85° 90°
Approach Angle A.A Approach Angle A.A
(Ex.) (1) A.R (Axial rake angle) = +10° }-> T.A. (Ex.) (1) A.R (Axial rake angle) =–10° }-> I (Inclination angle)
(2) R.R (Radial rake angle) = –30° (True rake angle) = –8° (4) (2) R.R (Radial rake angle) =+15° =–15° (4)
(3) A.A (Approach angle) = 60° (3) A.A (Approach angle) = 25°