Техническая информация Sumitomo - страница 15
Навигация
 Каталог Sumitomo пластины с алмазными вставками Sumidia
Каталог Sumitomo пластины с алмазными вставками Sumidia Общий каталог Sumitomo 2019 - 2020
Общий каталог Sumitomo 2019 - 2020 Каталог Sumitomo токарные резцы (державки) для наружного точения
Каталог Sumitomo токарные резцы (державки) для наружного точения Каталог Sumitomo твердосплавные пластины
Каталог Sumitomo твердосплавные пластины Каталог Sumitomo фрезы со сменными пластинами
Каталог Sumitomo фрезы со сменными пластинами Каталог Sumitomo пластины с режущей кромкой-моноалмаз Sumicristal
Каталог Sumitomo пластины с режущей кромкой-моноалмаз Sumicristal 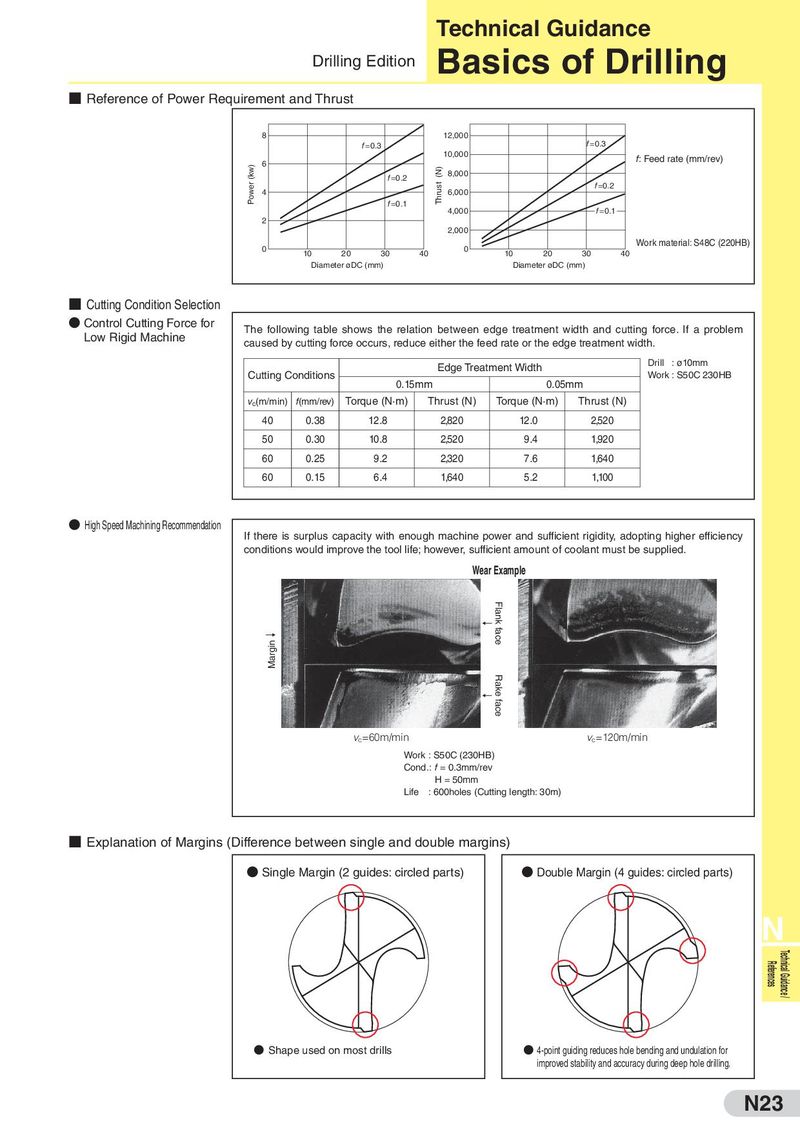
Technical Guidance Drilling Edition Basics of Drilling ■ Reference of Power Requirement and Thrust 8 12,000 f =0.3 f =0.3 10,000 f: Feed rate (mm/rev) (kw) 6 (N) f =0.2 8,000 Power 4 Thrust 6,000 f =0.2 f =0.1 f =0.1 4,000 2 2,000 0 0 Work material: S48C (220HB) 10 20 30 40 10 20 30 40 Diameter øDC (mm) Diameter øDC (mm) ■ Cutting Condition Selection ● Control Cutting Force for The following table shows the relation between edge treatment width and cutting force. If a problem Low Rigid Machine caused by cutting force occurs, reduce either the feed rate or the edge treatment width. Edge Treatment Width Drill : ø10mm Cutting Conditions Work : S50C 230HB 0.15mm 0.05mm vc(m/min) f(mm/rev) Torque (N·m) Thrust (N) Torque (N·m) Thrust (N) 40 0.38 12.8 2,820 12.0 2,520 50 0.30 10.8 2,520 9.4 1,920 60 0.25 9.2 2,320 7.6 1,640 60 0.15 6.4 1,640 5.2 1,100 ● High Speed Machining Recommendation If there is surplus capacity with enough machine power and sufficient rigidity, adopting higher efficiency conditions would improve the tool life; however, sufficient amount of coolant must be supplied. Wear Example ← Flank face → Margin ← Rake face vc=60m/min vc=120m/min Work : S50C (230HB) Cond.: f = 0.3mm/rev H = 50mm Life : 600holes (Cutting length: 30m) ■ Explanation of Margins (Difference between single and double margins) ● Single Margin (2 guides: circled parts) ● Double Margin (4 guides: circled parts) N References Technical Guidance / ● Shape used on most drills ● 4-point guiding reduces hole bending and undulation for improved stability and accuracy during deep hole drilling. N23