Техническая информация Sumitomo - страница 6
Навигация
 Каталог Sumitomo пластины с алмазными вставками Sumidia
Каталог Sumitomo пластины с алмазными вставками Sumidia Общий каталог Sumitomo 2019 - 2020
Общий каталог Sumitomo 2019 - 2020 Каталог Sumitomo токарные резцы (державки) для наружного точения
Каталог Sumitomo токарные резцы (державки) для наружного точения Каталог Sumitomo твердосплавные пластины
Каталог Sumitomo твердосплавные пластины Каталог Sumitomo фрезы со сменными пластинами
Каталог Sumitomo фрезы со сменными пластинами Каталог Sumitomo пластины с режущей кромкой-моноалмаз Sumicristal
Каталог Sumitomo пластины с режущей кромкой-моноалмаз Sumicristal 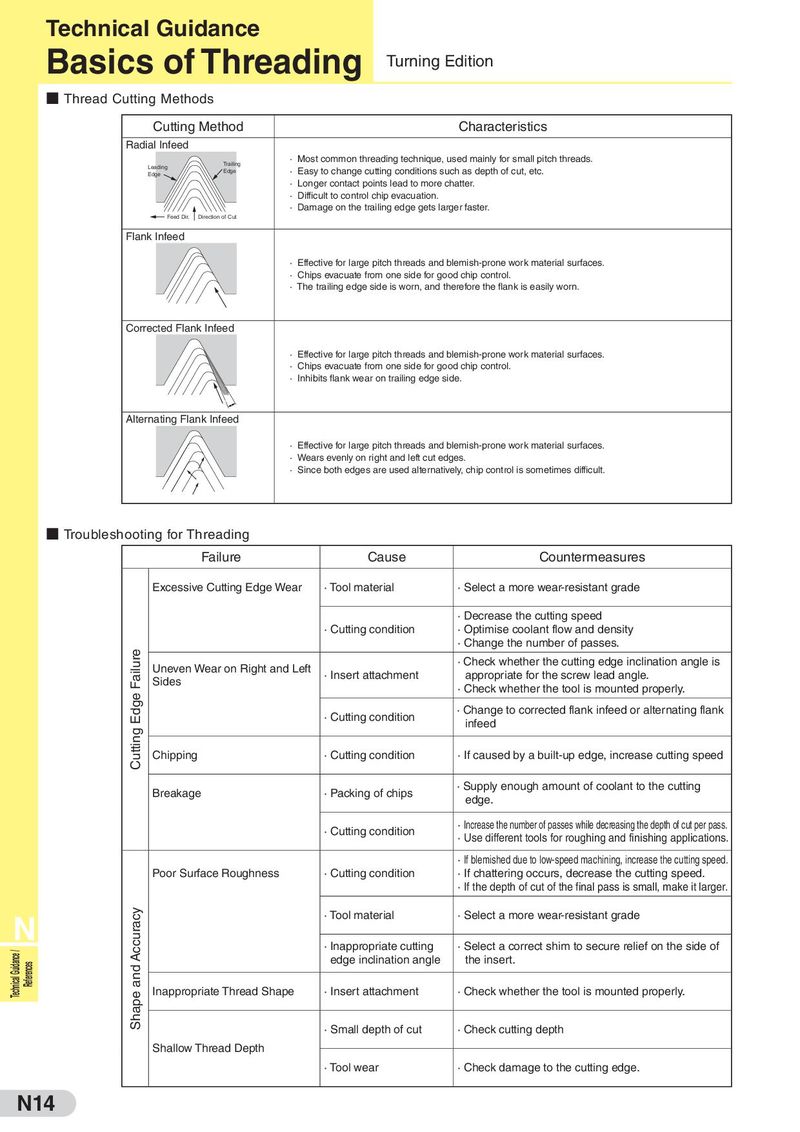
Technical Guidance Basics of Threading Turning Edition ■ Thread Cutting Methods Cutting Method Characteristics Radial Infeed Trailing · Most common threading technique, used mainly for small pitch threads. Leading Edge · Easy to change cutting conditions such as depth of cut, etc. Edge · Longer contact points lead to more chatter. · Difficult to control chip evacuation. · Damage on the trailing edge gets larger faster. Feed Dir. Direction of Cut Flank Infeed · Effective for large pitch threads and blemish-prone work material surfaces. · Chips evacuate from one side for good chip control. · The trailing edge side is worn, and therefore the flank is easily worn. Corrected Flank Infeed · Effective for large pitch threads and blemish-prone work material surfaces. · Chips evacuate from one side for good chip control. · Inhibits flank wear on trailing edge side. Alternating Flank Infeed · Effective for large pitch threads and blemish-prone work material surfaces. · Wears evenly on right and left cut edges. · Since both edges are used alternatively, chip control is sometimes difficult. ■ Troubleshooting for Threading Failure Cause Countermeasures Excessive Cutting Edge Wear · Tool material · Select a more wear-resistant grade · Decrease the cutting speed · Cutting condition · Optimise coolant flow and density · Change the number of passes. Cutting Edge Failure Uneven Wear on Right and Left · Check whether the cutting edge inclination angle is Sides · Insert attachment appropriate for the screw lead angle. · Check whether the tool is mounted properly. · Cutting condition · Change to corrected flank infeed or alternating flank infeed Chipping · Cutting condition · If caused by a built-up edge, increase cutting speed Breakage · Packing of chips · Supply enough amount of coolant to the cutting edge. · Cutting condition · Increase the number of passes while decreasing the depth of cut per pass. · Use different tools for roughing and finishing applications. · If blemished due to low-speed machining, increase the cutting speed. Poor Surface Roughness · Cutting condition · If chattering occurs, decrease the cutting speed. · If the depth of cut of the final pass is small, make it larger. N Shape and Accuracy · Tool material · Select a more wear-resistant grade Technical Guidance / · Inappropriate cutting · Select a correct shim to secure relief on the side of References edge inclination angle the insert. Inappropriate Thread Shape · Insert attachment · Check whether the tool is mounted properly. · Small depth of cut · Check cutting depth Shallow Thread Depth · Tool wear · Check damage to the cutting edge. N14