Техническая информация Sumitomo - страница 14
Навигация
 Каталог Sumitomo пластины с алмазными вставками Sumidia
Каталог Sumitomo пластины с алмазными вставками Sumidia Общий каталог Sumitomo 2019 - 2020
Общий каталог Sumitomo 2019 - 2020 Каталог Sumitomo токарные резцы (державки) для наружного точения
Каталог Sumitomo токарные резцы (державки) для наружного точения Каталог Sumitomo твердосплавные пластины
Каталог Sumitomo твердосплавные пластины Каталог Sumitomo фрезы со сменными пластинами
Каталог Sumitomo фрезы со сменными пластинами Каталог Sumitomo пластины с режущей кромкой-моноалмаз Sumicristal
Каталог Sumitomo пластины с режущей кромкой-моноалмаз Sumicristal 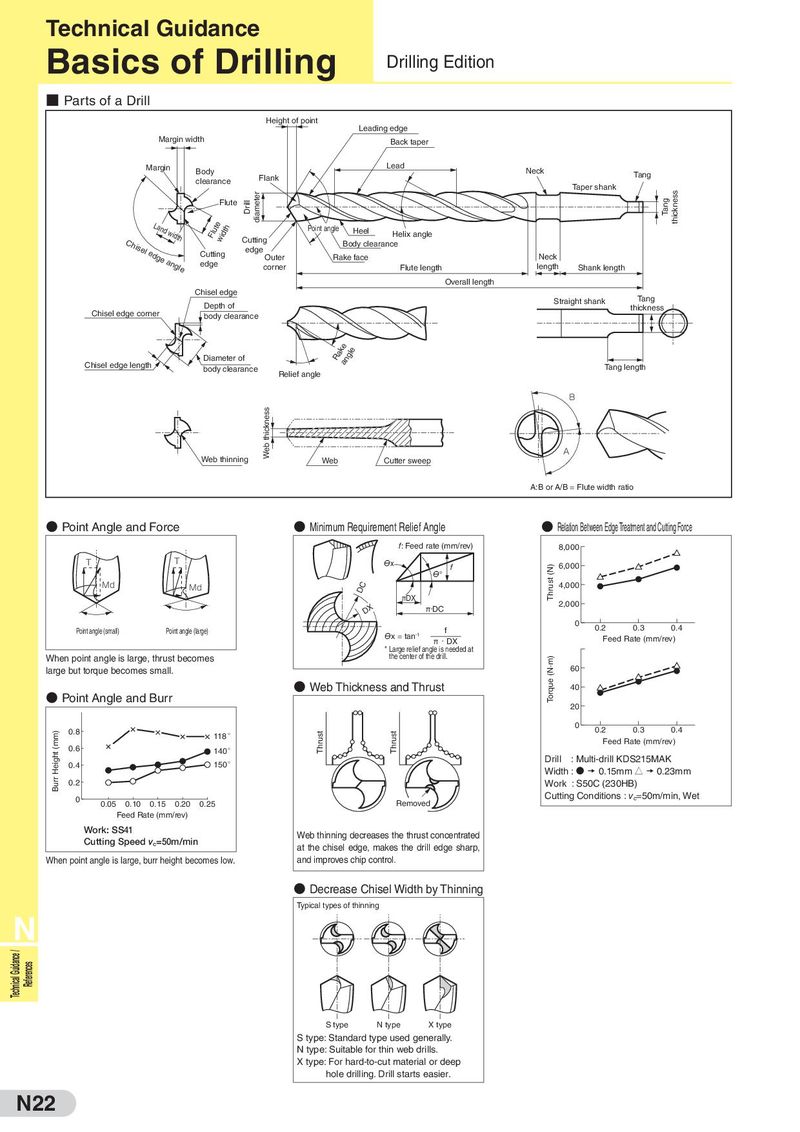
Technical Guidance Basics of Drilling Drilling Edition ■ Par ts of a Drill Height of point Leading edge Margin width Back taper Margin Body Lead Neck clearance Flank Tang Taper shank thickness Flute Drill diameter Tang Land width wiFldtuthe P先oin端t an角gle Heel Helix angle Chisel Cutting Body clearance edge angle Cutting edge Neck edge Outer Rake face corner Flute length length Shank length Overall length Chisel edge Tang Depth of Straight shank thickness Chisel edge corner body clearance Chisel edge length Diameter of anRglaeke body clearance Relief angle Tang length B Web thickness A Web thinning Web Cutter sweep A:B or A/B = Flute width ratio ● Point Angle and Force ● Minimum Requirement Relief Angle ● Relation Between Edge Treatment and Cutting Force f: Feed rate (mm/rev) 8,000 T T Ѳx f (N) 6,000 Ѳ° Thrust Md Md DC 4,000 πDX 2,000 DX π・DC 0 0.2 0.3 0.4 Point angle (small) Point angle (large) Ѳx = tan-1 f π・DX Feed Rate (mm/rev) * Large relief angle is needed at the center of the drill. When point angle is large, thrust becomes Torque (N·m) large but torque becomes small. 60 ● Web Thickness and Thrust 40 ● Point Angle and Burr 20 0.8 0 0.2 0.3 0.4 Height (mm) 118 ° Thrust Thrust Feed Rate (mm/rev) 0.6 140 ° 0.4 150 ° Drill : Multi-drill KDS215MAK Width : D 0.15mm J 0.23mm Burr 0.2 Work : S50C (230HB) 0 0.05 0.10 0.15 0.20 0.25 Removed Cutting Conditions : vc=50m/min, Wet Feed Rate (mm/rev) Work: SS41 Web thinning decreases the thrust concentrated Cutting Speed vc=50m/min at the chisel edge, makes the drill edge sharp, When point angle is large, burr height becomes low. and improves chip control. ● Decrease Chisel Width by Thinning Typical types of thinning N Technical Guidance / References S type N type X type S type: Standard type used generally. N type: Suitable for thin web drills. X type: For hard-to-cut material or deep hole drilling. Drill starts easier. N22