Каталог Widia трохоидальное фрезерование - страница 87
Навигация
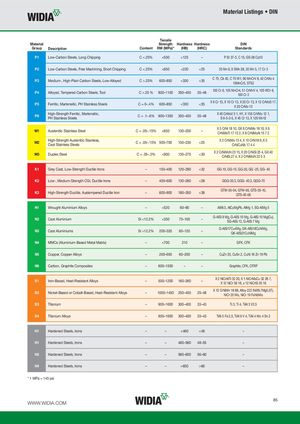
Material Listings • DIN Tensile Material Strength Hardness Hardness DIN Group Description Content RM (MPa)* (HB) (HRC) Standards P1 Low-Carbon Steels, Long Chipping C <.25% <530 <125 – P St 37-3, C 15, GS-38 Cq10 P2 Low-Carbon Steels, Free Machining, Short Chipping C <.25% <650 <220 <25 33 Mn 6, 9 SMn 28, 20 Mn 5, 17 Cr 3 P3 Medium-, High-Plain Carbon Steels, Low-Alloyed C >.25% 600–850 <330 <35 C 75, Ck 45, C 70 W1, 90 MnCrV 8, 42 CrMo 416MnCr5, ST52 P4 Alloyed, Tempered Carbon Steels, Tool C >.25 % 800–1100 350–450 35–48 100 Cr 6, 105 MnCr4, 51 CrMnV 4, 105 WCr 6,100 Cr 2 P5 Ferritic, Martensitic, PH Stainless Steels C = 0–.4% 600–850 <330 <35 X 6 Cr 13, X 10 Cr 13, X 20 Cr 13, X 12 CrMoS 17,X 20 CrMo 13 P6 High-Strength Ferritic, Martensitic,PH Stainless Steels C = .1–.6% 900–1350 350–450 35–48 X 40 CrMoV 5 1, H1, X 155 CrVMo 12 1,S 6-5-2-5, X 45 Cr 13, X 120 Mn12 M1 Austenitic Stainless Steel C = .05–.15% <650 130–200 – X 5 CrNi 18 10, GX 6 CrNiMo 18 10, X 6CrNiMoTi 17 12 2, X 8 CrNiMoAl 15 7 2 M2 High-Strength Austenitic Stainless,Cast Stainless Steels C = .05–.15% 500–700 150–230 <25 X 2 CrNiMo 13 4, X 10 CrNi18 9, X 5CrNiCuNb 17 4 4 M3 Duplex Steel C = .05–.2% <900 135–275 <30 X 2 CrNiMoN 23 15, X 20 CrNiSi 25 4, GX 40CrNiSi 27 4, X 2 CrNiMoN 22 5 3 K1 Grey Cast, Low-Strength Ductile Irons – 150–400 120–290 <32 GG-10, GG-15, GG-20, GG -25, GG- 40 K2 Low-, Medium-Strength CGI, Ductile Irons – 400–600 130–260 <28 GGG-35.3, GGG- 40.3, GGG-70 K3 High-Strength Ductile, Austempered Ductile Iron – 600–900 180–350 <38 GTW-35-04, GTW-65, GTS-35-10,GTS-45-06 N1 Wrought Aluminium Alloys – <520 60–90 – Al99.5, AlCuMgPb, AlMg 1, SG-AlMg 5 N2 Cast Aluminium Si <12.2% <350 70–100 – G-AlSi 9 Mg, G-AlSi 10 Mg, G-AlSi 10 Mg(Cu),SG-AlSi 12, G-AlSi 7 Mg N3 Cast Aluminiums Si >12.2% 200–320 60–120 – G-AlSi17Cu4Mg, GK-AlSi18CuNiMg,GK-AlSi21CuNiMg N4 MMCs (Aluminium-Based Metal Matrix) – <700 210 – GFK, CFK N5 Copper, Copper Alloys – 200–650 60–200 – CuZn 20, CuSn 2, CuNi 18 Zn 19 Pb N6 Carbon, Graphite Composites – 600–1500 – – Graphite, CFK, CFRP S1 Iron-Based, Heat-Resistant Alloys – 500–1200 160–260 – X 2 NiCrAlTi 32 20, X 1 NiCrMoCu 32 28 7,X 12 NiCr 36 18, x 12 NiCrSi 35 16 S2 Nickel-Based or Cobalt-Based, Heat-Resistant Alloys – 1000–1450 250–450 25–48 X 12 CrNiMn 18 88, Alloy 222 (Ni99,7Mg0,07),NiCr 20 Mo, NiCr 19 FeNbMo S3 Titanium – 900–1600 300–400 33–43 Ti 3, Ti 4, TiAl 3 V2.5 S4 Titanium Alloys – 900–1600 300–400 33–43 TiAl 5 Fe 2,5, TiAl 6 V 4, TiAl 4 Mo 4 Sn 2 H1 Hardened Steels, Irons – – <460 <48 – H1 Hardened Steels, Irons – – 460–560 48–55 – H2 Hardened Steels, Irons – – 560–650 56–60 – H4 Hardened Steels, Irons – – >650 >60 – * 1 MPa = 145 psi WWW.WIDIA.COM 85
 Каталог Widia достижения 2021
Каталог Widia достижения 2021 Каталог Widia токарный инструмент 2017
Каталог Widia токарный инструмент 2017 Брошюра Widia техническое руководство
Брошюра Widia техническое руководство Каталог Widia инструмент для обработки отверстий 2017
Каталог Widia инструмент для обработки отверстий 2017 Каталог Widia техническое руководство по разверткам
Каталог Widia техническое руководство по разверткам