Основной каталог Kyocera 2016-2017 - страница 950
Навигация
 Каталог Kyocera фрезы MFH для высокоскоростной обработки
Каталог Kyocera фрезы MFH для высокоскоростной обработки Каталог Kyocera фрезы MEC высокопроизводительные концевые и торцевые фрезы
Каталог Kyocera фрезы MEC высокопроизводительные концевые и торцевые фрезы Каталог микроинструмента Kyocera 2015-2016
Каталог микроинструмента Kyocera 2015-2016 Каталог Kyocera высокоэффективные сверла со сменными пластинами DRV
Каталог Kyocera высокоэффективные сверла со сменными пластинами DRV Каталог Kyocera пластины TQ для нарезания резьбы c прессованным стружколомом
Каталог Kyocera пластины TQ для нарезания резьбы c прессованным стружколомом Каталог Kyocera высокопроизводительные модульные сверла DRA
Каталог Kyocera высокопроизводительные модульные сверла DRA 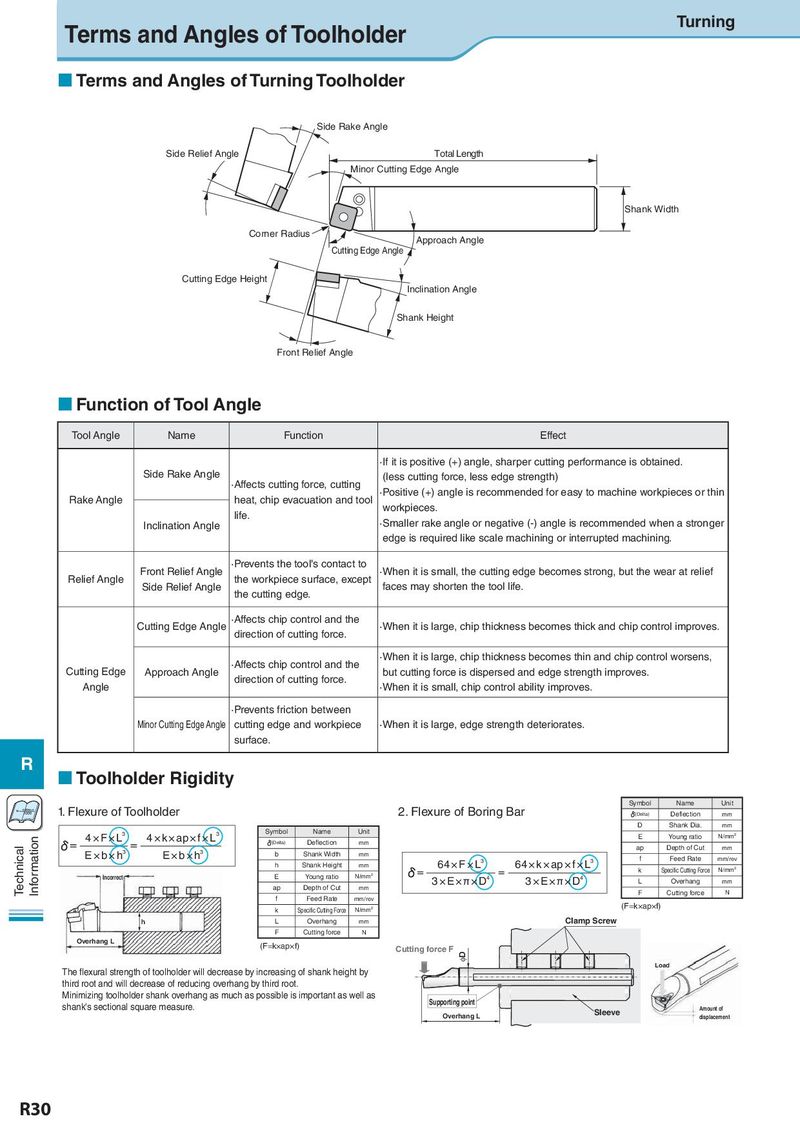
Terms and Angles of Toolholder Turning Terms and Angles of Turning Toolholder Side Rake Angle Side Relief Angle Total Length Minor Cutting Edge Angle Shank Width Corner Radius Approach Angle Cutting Edge Angle Cutting Edge Height Inclination Angle Shank Height Front Relief Angle Function of Tool Angle Tool Angle Name Function Effect ·If it is positive (+) angle, sharper cutting performance is obtained. Side Rake Angle (less cutting force, less edge strength) ·Affects cutting force, cutting ·Positive (+) angle is recommended for easy to machine workpieces or thin Rake Angle heat, chip evacuation and tool workpieces. life. ·Smaller rake angle or negative (-) angle is recommended when a stronger Inclination Angle edge is required like scale machining or interrupted machining. Front Relief Angle ·Prevents the tool's contact to ·When it is small, the cutting edge becomes strong, but the wear at relief Relief Angle Side Relief Angle the workpiece surface, except faces may shorten the tool life. the cutting edge. Cutting Edge Angle ·Affects chip control and the ·When it is large, chip thickness becomes thick and chip control improves. direction of cutting force. ·Affects chip control and the ·When it is large, chip thickness becomes thin and chip control worsens, Cutting Edge Approach Angle direction of cutting force. but cutting force is dispersed and edge strength improves. Angle ·When it is small, chip control ability improves. ·Prevents friction between Minor Cutting Edge Angle cutting edge and workpiece ·When it is large, edge strength deteriorates. surface. R Toolholder Rigidity Symbol Name Unit Vc= π×Dm×n 1. Flexure of Toolholder 2. Flexure of Boring Bar (Delta) Deflection mm D Shank Dia. mm 4 × F × L3 4 × k × ap × f × L3 Symbol Name Unit E Young ratio N/mm2 Information (Delta) Deflection mm ap Depth of Cut Technical E × b × h3 E × b × h3 mm b Shank Width mm f Feed Rate mm/rev h Shank Height mm 64 × F × L3 64 × k × ap × f × L3 k Specific Cutting Force N/mm2 Incorrect E Young ratio N/mm2 3 × E × π × D4 3 × E × π × D4 L Overhang mm ap Depth of Cut mm F Cutting force N f Feed Rate mm/rev k Specific Cutting Force N/mm2 (F=k×ap×f) h L Overhang mm Clamp Screw F Cutting force N Overhang L (F=k×ap×f) Cutting force F φD The flexural strength of toolholder will decrease by increasing of shank height by Load third root and will decrease of reducing overhang by third root. Minimizing toolholder shank overhang as much as possible is important as well as Supporting point shank's sectional square measure. Sleeve Amount of Overhang L displacement R30