Общий каталог Sumitomo 2018 - 2019 - страница 562
Навигация
- Pages 3-6_CS6_EN_web
- A 1-20 insert selection EN_web
- B 1-14 grades_EN_web
- C01-17 inserts intro pages_EN_web
- C18-56 negative inserts_EN_web
- C57-86 positive inserts_EN_web
- D 1-46 tool holders_EN_web
- E 1-24 boring bars_EN_web
- F 1-48 grooving_thread tools_EN_web
- G 1-54 milling cutters_EN_web
- H 1-48 insert type endmills_EN_web
- J 1-24 new endmills_EN_web
- J 25-50 endmills_EN_web
- K 1-46 Multi-Drills_EN_web
- K 47-76 Multi-Drills_EN_web
- L 1-28 cbn_pcd grades_EN_web
- M 1-34 cbn_pcd inserts_EN_web
- M 35-56 SHM tools_EN_web
- N1-24 technical guidance_EN_web
- P 1-8 spare parts_neu_EN_web
- P 9-22 index_notes_EN_web
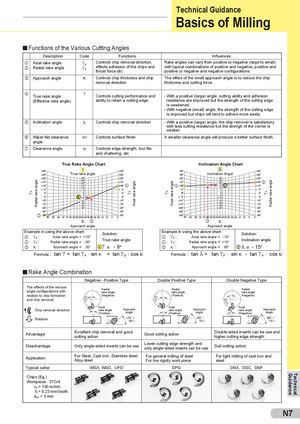
γx Radial rake angle γy Axial rake angle γy Axial rake angle γx Radial rake angle Technical Guidance Basics of Milling Functions of the Various Cutting Angles Description Code Functions Influences j Axial rake anglekRadial rake angle γyγx Controls chip removal direction,effects adhesion of the chips andthrust force etc.Rake angles can vary from positive to negative (large to small)with typical combinations of positive and negative, positive andpositive or negative and negative configurations. l Approach angle κ Controls chip thickness and chip The effect of the small approach angle is to reduce the chip removal direction thickness and cutting force. m True rake angle γ Controls cutting performance and - With a positive (large) angle, cutting ability and adhesion (Effective rake angle) ability to retain a cutting edge resistance are improved but the strength of the cutting edge is weakened. - With negative (small) angle, the strength of the cutting edge is improved but chips will tend to adhere more easily. n Inclination angle λ Controls chip removal direction - With a positive (large) angle, the chip removal is satisfactory with less cutting resistance but the strengh of the corner is weaker. o Wiper flat clearance αf Controls surface finish A smaller clearance angle will produce a better surface finish. angle p Clearance angle α Controls edge strength, tool life and chattering, etc True Rake Angle Chart Inclination Angle Chart γ λ True rake angle Inclination Angel j j n k m k κ l l κ Approach angle Approach angle Example in using the above chart:jγy :Axial rake angle=+10°kγx :Radial rake angle =-30°lκ:Approach angle =30°Solution:True rake anglemγ =- 8oExample in using the above chart :jγy :Axial rake angle =-10°kγx :Radial rake angle=+10°Solution:Inclination anglelκ:Approach angle =65°nλ =- 15° Formula : tan γ = tan γ x . sin κ + tan γ y . cos κ Formula : tan λ = tan γ y . sin κ - tan γ x . cos κ Rake Angle Combination Negative - Positive Type Double Positive Type Double Negative Type The effects of the variousangle configurations with Radialrake angle Radialrake angle Radialrake angle relation to chip formation (Negative) (Positive) (Negative) and chip removal. Chip removal direction Axialrake angle(Positive)Approachangle Axialrake angle(Positive) Approachangle Axialrake angle(Negative)Approachangle Rotation (45° ~ (60° ~ (60° ~60°)75°)75°) Advantage Excellent chip removal and goodcutting action Good cutting action Double-sided inserts can be use andhigher cutting edge strength Disadvantage Only single-sided inserts can be use Lower cutting edge strength andonly single-sided inserts can be useDull cutting action Application For Steel, Cast iron, Stainless steel, For general milling of steel For light milling of cast iron andAlloy steelFor low rigidly work piecesteel Typical cutter WGX, WGC, UFO DPG DNX, DGC, DNF Chips (Eg.) Workpiece: 37Cr4 vc = 130 m/min f t = 0.23 mm/ tooth doc = 3 mm N7 Guidance Technical
 Общий каталог Sumitomo 2012
Общий каталог Sumitomo 2012 Каталог Sumitomo резьбонарезной инструмент
Каталог Sumitomo резьбонарезной инструмент Каталог Sumitomo пластины с режущей кромкой-моноалмаз Sumicristal
Каталог Sumitomo пластины с режущей кромкой-моноалмаз Sumicristal Каталог Sumitomo инструмент для обработки канавок
Каталог Sumitomo инструмент для обработки канавок Общий каталог Sumitomo 2019 - 2020
Общий каталог Sumitomo 2019 - 2020 Каталог Sumitomo запасные части
Каталог Sumitomo запасные части