Основной каталог Kyocera 2016-2017 - страница 924
Навигация
 Каталог Kyocera фрезы MFH для высокоскоростной обработки
Каталог Kyocera фрезы MFH для высокоскоростной обработки Каталог Kyocera фрезы MEC высокопроизводительные концевые и торцевые фрезы
Каталог Kyocera фрезы MEC высокопроизводительные концевые и торцевые фрезы Каталог микроинструмента Kyocera 2015-2016
Каталог микроинструмента Kyocera 2015-2016 Каталог Kyocera высокоэффективные сверла со сменными пластинами DRV
Каталог Kyocera высокоэффективные сверла со сменными пластинами DRV Каталог Kyocera пластины TQ для нарезания резьбы c прессованным стружколомом
Каталог Kyocera пластины TQ для нарезания резьбы c прессованным стружколомом Каталог Kyocera высокопроизводительные модульные сверла DRA
Каталог Kyocera высокопроизводительные модульные сверла DRA 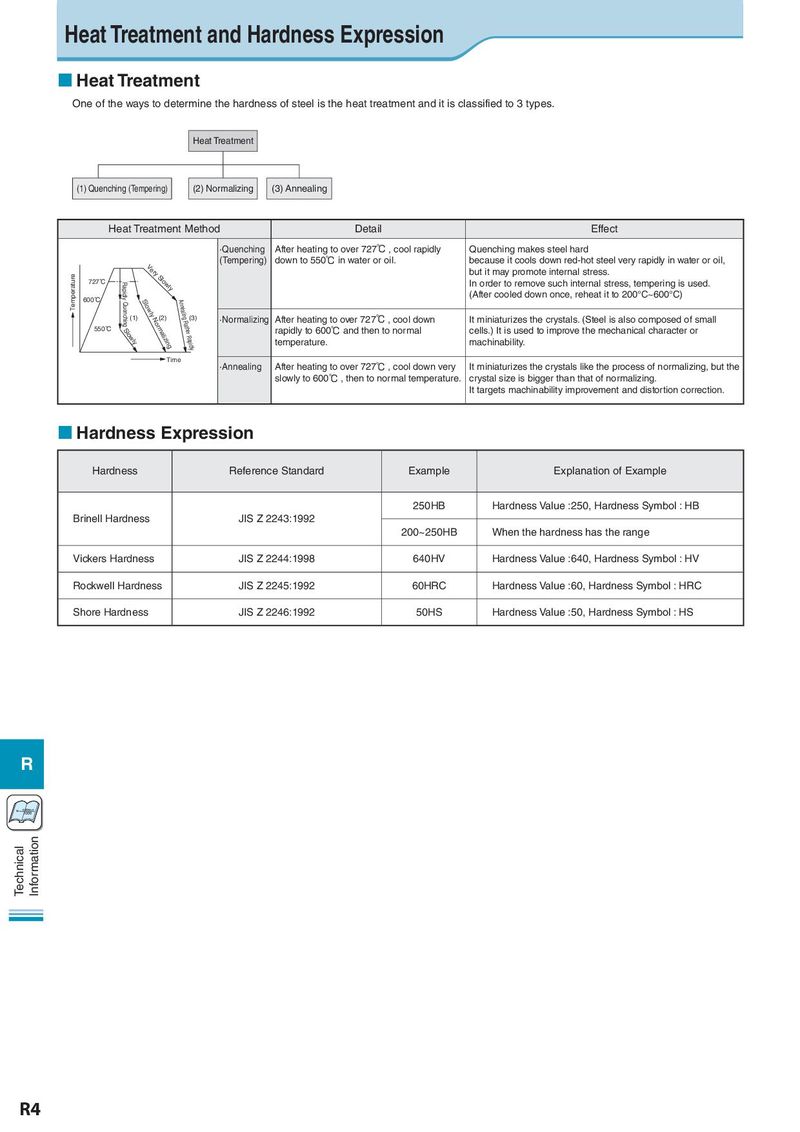
Heat Treatment and Hardness Expression Heat Treatment One of the ways to determine the hardness of steel is the heat treatment and it is classified to 3 types. Heat Treatment (1) Quenching (Tempering) (2) Normalizing (3) Annealing Heat Treatment Method Detail Effect ·Quenching After heating to over 727℃ , cool rapidly Quenching makes steel hard Very Slowly (Tempering) down to 550℃ in water or oil. because it cools down red-hot steel very rapidly in water or oil, Temperature Rapidly but it may promote internal stress. 727˚C Rapidly Quenching Slowly In order to remove such internal stress, tempering is used. 600˚C (After cooled down once, reheat it to 200°C~600°C) (1) Slowly Normalizing(2)Annealing Rather Rapidly(3) ·Normalizing After heating to over 727℃ , cool down It miniaturizes the crystals. (Steel is also composed of small 550˚C rapidly to 600℃ and then to normal cells.) It is used to improve the mechanical character or temperature. machinability. Time ·Annealing After heating to over 727℃ , cool down very It miniaturizes the crystals like the process of normalizing, but the slowly to 600℃ , then to normal temperature. crystal size is bigger than that of normalizing. It targets machinability improvement and distortion correction. Hardness Expression Hardness Reference Standard Example Explanation of Example 250HB Hardness Value :250, Hardness Symbol : HB Brinell Hardness JIS Z 2243:1992 200~250HB When the hardness has the range Vickers Hardness JIS Z 2244:1998 640HV Hardness Value :640, Hardness Symbol : HV Rockwell Hardness JIS Z 2245:1992 60HRC Hardness Value :60, Hardness Symbol : HRC Shore Hardness JIS Z 2246:1992 50HS Hardness Value :50, Hardness Symbol : HS R Vc= π×Dm×n Technical Information R4