Общий каталог Yamawa 2021 - страница 706
Навигация
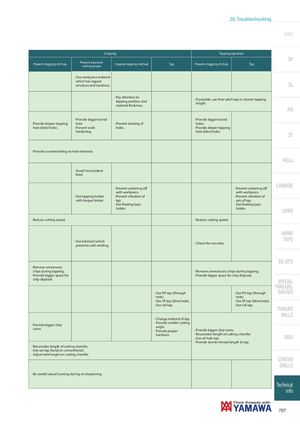
20. Troubleshooting Intro Chipping Tapping operation SP Prevent clogging of chips Prevent excessivecutting torqueImprove tapping method Tap Prevent clogging of chips Tap ∙ Use workpiece material which has regularstructure and hardness. SL ∙ Pay attention totapping position andmaterial thickness.∙ If possible, use finer pitch tap or shorter tappinglength. PO ∙ Provide bigger bored ∙ Provide bigger bored ∙ Provide deeper tapping hole. ∙ Prevent slanting of holes. hole (blind hole). ∙ Prevent work holes. ∙ Provide deeper tapping hardening. hole (blind hole). ST ∙ Provide countersinking on hole entrance. ROLL ∙ Avoid inconsistent feed. ∙ Prevent centering-off ∙ Prevent centering-off CARBIDE with workpiece. with workpiece. ∙ Use tapping holder ∙ Prevent vibration of ∙ Prevent vibration of with torque limiter. tap. axis of tap. ∙ Use floating type ∙ Use floating type holder. holder. LONG ∙ Reduce cutting speed. ∙ Reduce cutting speed. HAND ∙ Use lubricant whichprevents cold welding. TAPS∙ Check the viscosity. EG (STI) ∙ Remove unncessary chips during tapping. ∙ Remove unnecessary chips during tapping. ∙ Provide bigger space for ∙ Provide bigger space for chip disposal. chip disposal. SPECIAL THREADS, ∙ Use PO tap (through ∙ Use PO tap (through GAUGES hole). hole). ∙ Use SP tap (blind hole). ∙ Use SP tap (blind hole). ∙ Use roll tap. ∙ Use roll tap. THREAD MILLS ∙ Change material of tap. ∙ Provide bigger chiproom. ∙ Provide smaller cuttingangle.∙ Provide proper∙ Provide bigger chip room. hardness. ∙ Reconsider length of cutting chamfer.∙ Use oil hole tap. DIES ∙ Provide shorter thread length to tap. ∙ Reconsider length of cutting chamfer. ∙ Use set tap (Serial or conventional). ∙ Adjust relief angle on cutting chamfer. CENTER DRILLS ∙ Be careful about burning during re-sharpening Technical info 707
 Обший каталог Yamawa 2016 - 2017
Обший каталог Yamawa 2016 - 2017 Краткое руководство Yamawa по каталогам
Краткое руководство Yamawa по каталогам Общий каталог Yamawa 2022 - 2023
Общий каталог Yamawa 2022 - 2023 Каталоги Yamawa твердосплавные метчики для закаленной стали
Каталоги Yamawa твердосплавные метчики для закаленной стали