Общий каталог Mitsubishi 2020 - 2021 - страница 1729
Навигация
 Каталог Mitsubishi Materials запасные части
Каталог Mitsubishi Materials запасные части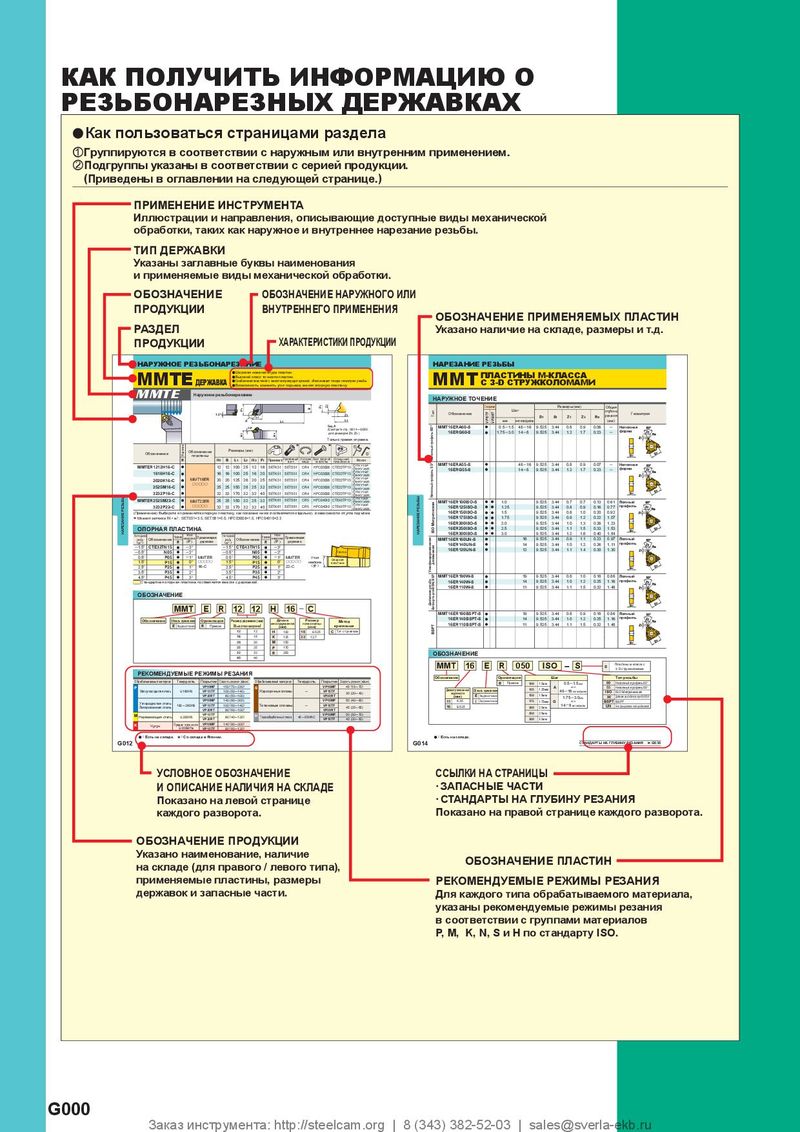 Каталог Mitsubishi Materials резьбонарезной инструмент
Каталог Mitsubishi Materials резьбонарезной инструмент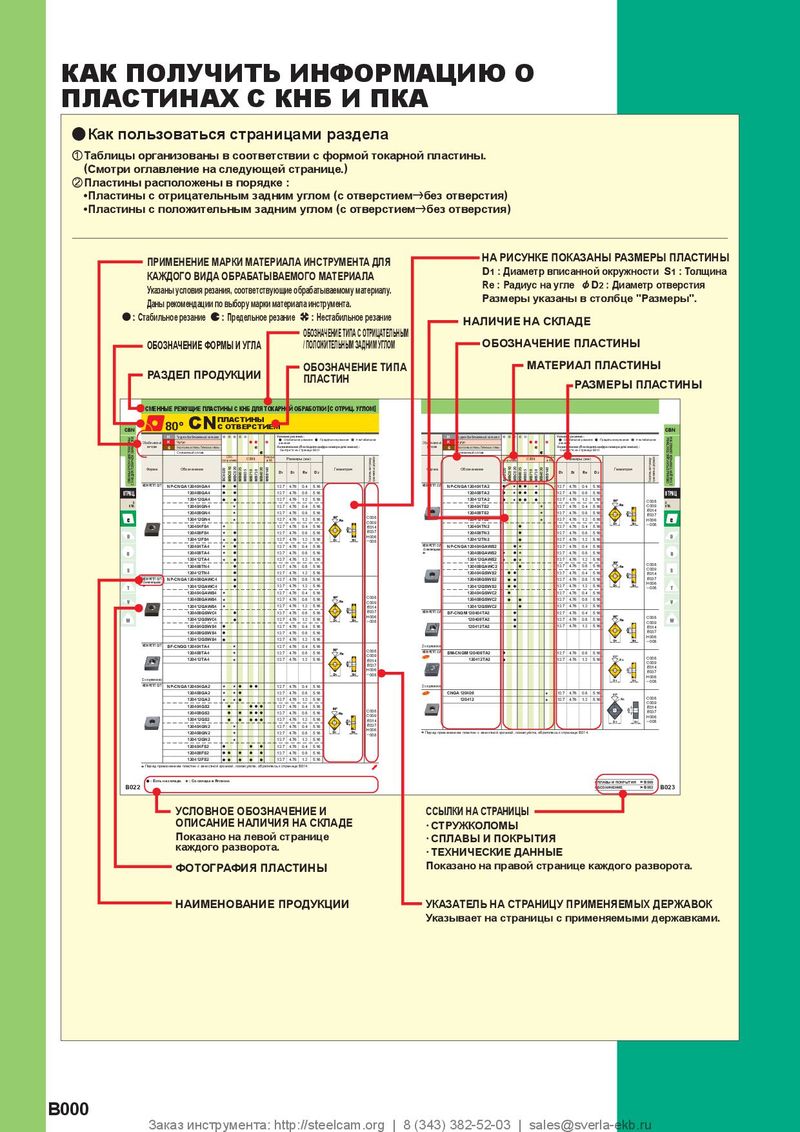 Каталог Mitsubishi Materials СНП с CBN и PCD для токарной обработки
Каталог Mitsubishi Materials СНП с CBN и PCD для токарной обработки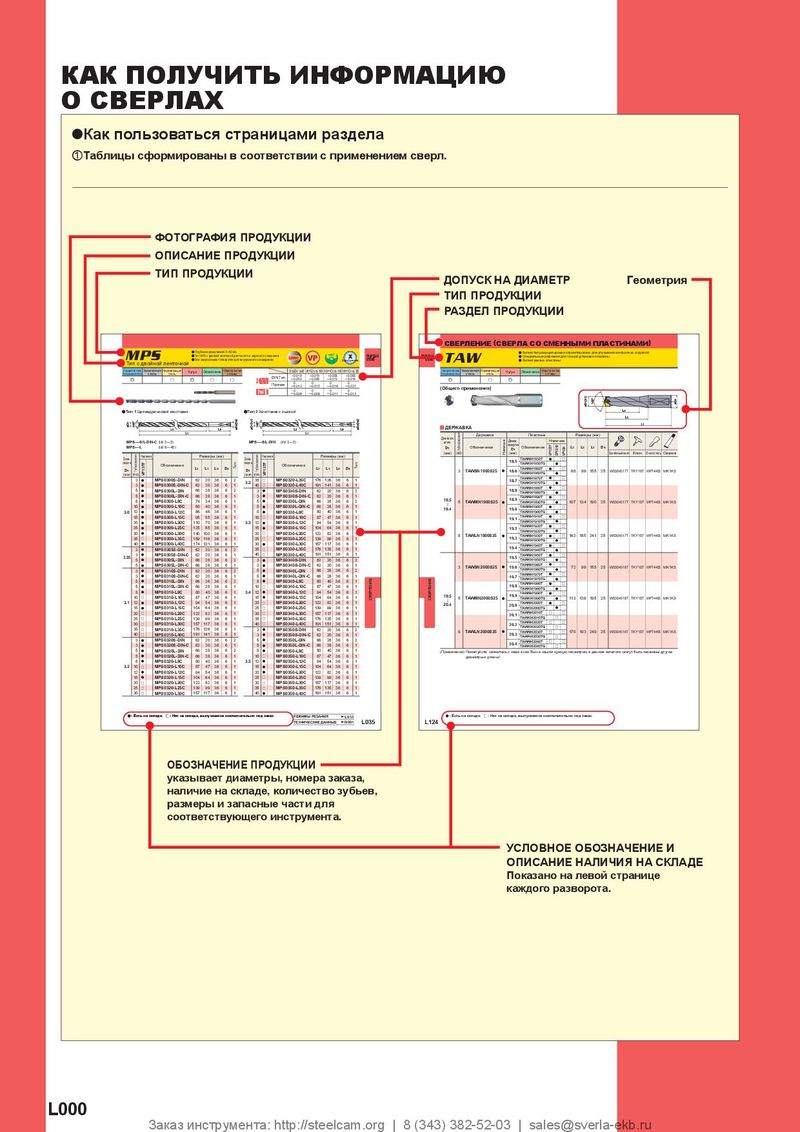 Каталог Mitsubishi Materials сверлильные инструменты
Каталог Mitsubishi Materials сверлильные инструменты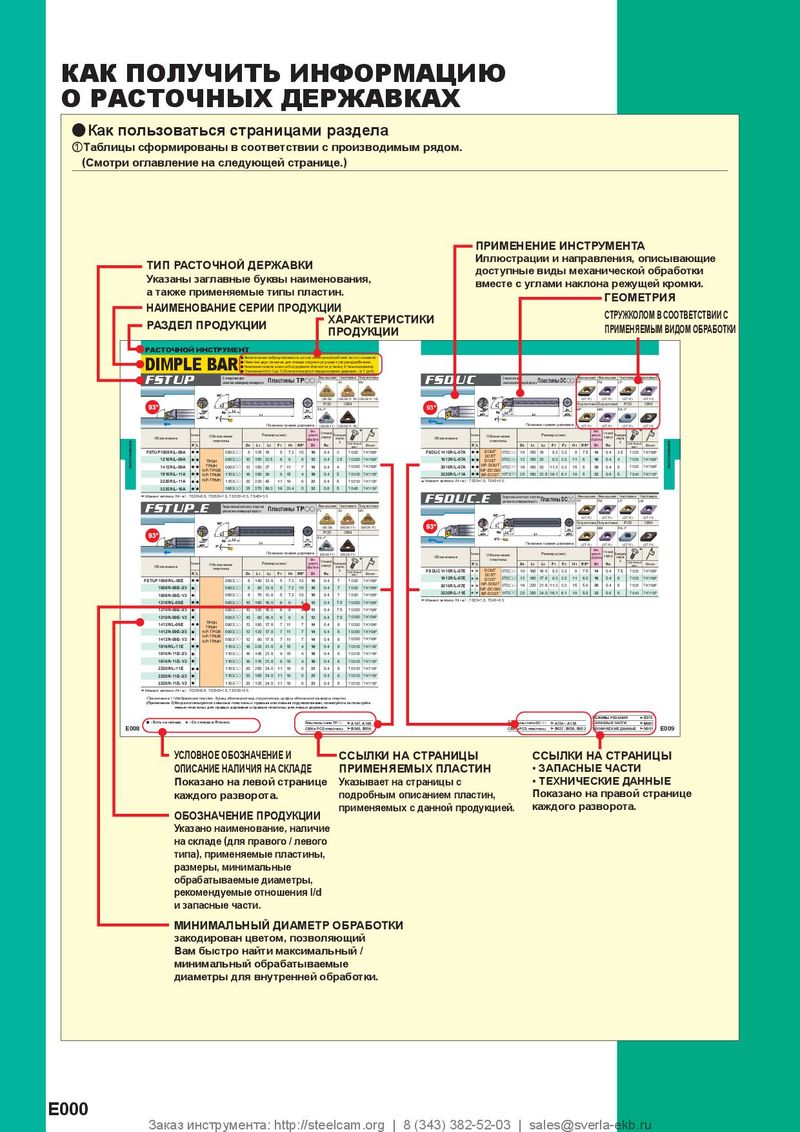 Каталог Mitsubishi Materials расточной инструмент
Каталог Mitsubishi Materials расточной инструмент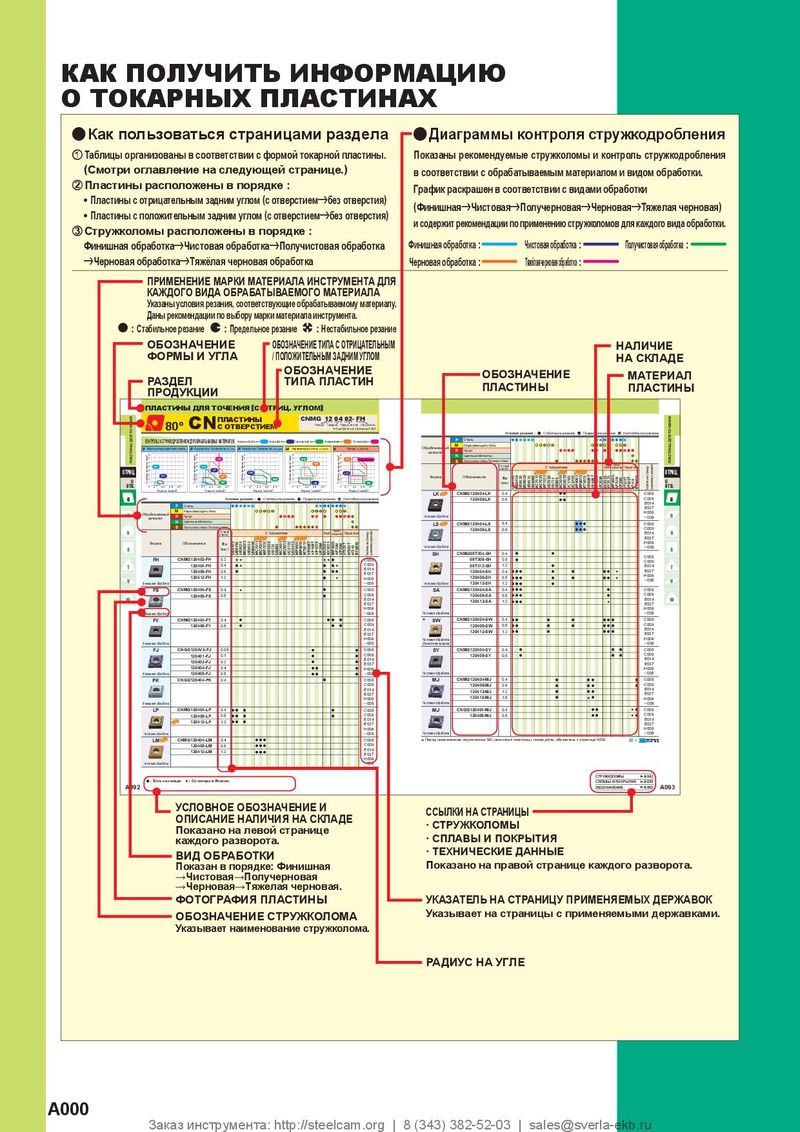 Каталог Mitsubishi Materials пластины для точения
Каталог Mitsubishi Materials пластины для точения 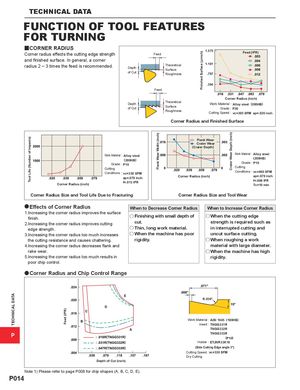
TECHNICAL DATA Tool Life (Number of Impacts) Feed (IPR) Flank Wear Width (inch) Finished Surface (!inch) Crater Wear Depth (inch) TECHNICAL DATA FUNCTION OF TOOL FEATURES FOR TURNING yCORNER RADIUSCorner radius effects the cutting edge strength Feed 1.575 Feed (IPR) and finished surface. In general, a corner radius 2 ― 3 times the feed is recommended. Depth Theoretical 1.181Surface of Cut Roughness .787 .394 Feed Corner Radius (inch) Depthof Cut TheoreticalSurfaceRoughness Work Material : Alloy steel (200HB)Grade : P20Cutting Speed :vc=395 SFMap=.020 inch Corner Radius and Finished Surface Flank Wear Crater Wear (Crater Depth) Work Material : Alloy steel(280HB)Grade : P10Cutting Work Material : Alloy steel(200HB)Grade : P10Cutting Conditions : vc=330 SFM Conditions : vc=460 SFM ap=.079 inch Corner Radius (inch) ap=.079 inch Corner Radius (inch) f=.013 IPR f=.008 IPRTc=10 min Corner Radius Size and Tool Life Due to Fracturing Corner Radius Size and Tool Wear aEffects of Corner Radius When to Decrease Corner Radius When to Increase Corner Radius 1.Increasing the corner radius improves the surface finish. u Finishing with small depth of u When the cutting edge 2.Increasing the corner radius improves cutting cut. strength is required such as edge strength. u Thin, long work material. in interrupted cutting and 3.Increasing the corner radius too much increases u When the machine has poor uncut surface cutting. the cutting resistance and causes chattering. rigidity. u When roughing a work 4.Increasing the corner radius decreases flank and material with large diameter. rake wear. u When the machine has high 5.Increasing the corner radius too much results in rigidity. poor chip control. a Corner Radius and Chip Control Range R.039" Work Material : AISI 1045 (180HB) Insert : TNGG331R TNGG332R P TNGG333R (P10) Holder : ETJNR33K16 (Side Cutting Edge angle 3°) Cutting Speed : vc=330 SFM Dry Cutting Depth of Cut (inch) Note 1) Please refer to page P008 for chip shapes (A, B, C, D, E). P014