Общий каталог Yamawa 2021 - страница 641
Навигация
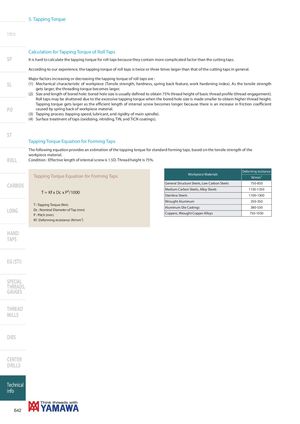
5. Tapping Torque Intro Calculation for Tapping Torque of Roll Taps SP It is hard to calculate the tapping torque for roll taps because they contain more complicated factor than the cutting taps. According to our experience, the tapping torque of roll taps is twice or three times larger than that of the cutting taps in general. Major factors increasing or decreasing the tapping torque of roll taps are : SL (1) Mechanical characteristic of workpiece (Tensile strength, hardness, spring back feature, work hardening index). As the tensile strength gets larger, the threading torque becomes larger. (2) Size and length of bored hole: bored hole size is usually defined to obtain 75% thread height of basic thread profile (thread engagement). Roll taps may be shuttered due to the excessive tapping torque when the bored hole size is made smaller to obtain higher thread height. Tapping torque gets larger as the efficient length of internal screw becomes longer because there is an increase in friction coefficient PO caused by spring back of workpiece material. (3) Tapping process (tapping speed, lubricant, and rigidity of main spindle). (4) Surface treatment of taps (oxidizing, nitriding, TiN, and TiCN coatings). ST Tapping Torque Equation for Forming Taps The following equation provides an estimation of the tapping torque for standard forming taps, based on the tensile strength of the workpiece material. ROLL Condition : Effective length of internal screw is 1.5D. Thread height is 75%. Deforming resistance Tapping Torque Equation for Forming Taps Workpiece Materials N/mm2 CARBIDE General Structure Steels, Low Carbon Steels 750-850 Medium Carbon Steels, Alloy Steels 1150-1350 T = Kf x Dc x P2/1000 Stainless Steels 1100-1300 Wrought Aluminum 250-350 T : Tapping Torque (Nm) Aluminum Die Castings 380-530 LONG Dc : Nominal Diameter of Tap (mm)P : Pitch (mm) Coppers, Wrought Copper Alloys 750-1050 Kf : Deforming resistance (N/mm2) HAND TAPS EG (STI) SPECIAL THREADS, GAUGES THREAD MILLS DIES CENTER DRILLS Technical info 642
 Обший каталог Yamawa 2016 - 2017
Обший каталог Yamawa 2016 - 2017 Краткое руководство Yamawa по каталогам
Краткое руководство Yamawa по каталогам Общий каталог Yamawa 2022 - 2023
Общий каталог Yamawa 2022 - 2023 Каталоги Yamawa твердосплавные метчики для закаленной стали
Каталоги Yamawa твердосплавные метчики для закаленной стали