Общий каталог Yamawa 2021 - страница 639
Навигация
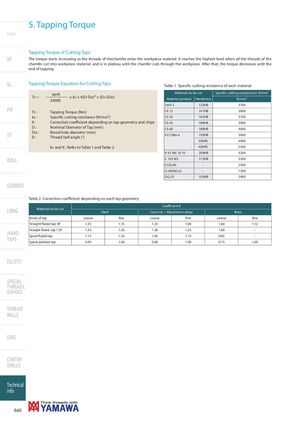
5. Tapping Torque Intro Tapping Torque of Cutting Taps SP The torque starts increasing as the threads of thechamfer enter the workpiece material. It reaches the highest level when all the threads of the chamfer cut into workpiece material, and is in plateau until the chamfer cuts through the workpiece. After that, the torque decreases until the end of tapping. SL Tapping Torque Equation for Cutting Taps Table 1 Specific cutting resistance of each material Tc = tanθ . x kc × K(D-Do)² × (D+2Do)24000 Materials to be cut Specific cutting resistance kc N/mm2Material symbolsHardenessN/mm2 5t44-2 133HB 3700 PO Tc : Tapping Torque (Nm) Ck 15 141HB 3600 kc : Specific cutting resistance (N/mm2) Ck 35 162HB 3700 K: Correction coefficient depending on tap geometry and chips Ck 45 188HB 3900 D: Nominal Diameter of Tap (mm) Ck 60 188HB 4000 ST Do : Bored hole diameter (mm)θ:Thread half angle (°) 42 CrMo 4 193HB 3600 30HRC 4900 kc and K : Refer to Table 1 and Table 2 40HRC 5500 X 6 CrNi 18 10 209HB 4200 ROLL C 105 W2 175HB 5300 CnZn40 - 2300 G-AISi8Cu3 - 1300 GG-25 193HB 2900 CARBIDE Table 2 Correction coefficient depending on each tap geometry Coefficient K LONG Materials to be cut Steel Cast iron + Alluminium alloys Brass Kinds of tap coarse fine coarse fine coarse fine Straight fluted tap 5P 1.35 1.15 1.25 1.08 1.60 1.12 HANDTAPS Straight fluted tap 1.5PSpiral fluted tapSpiral pointed tap1.431.150.951.501.251.001.301.050.80 1.251.101.00 1.680.850.75 --1.00 EG (STI) SPECIAL THREADS, GAUGES THREAD MILLS DIES CENTER DRILLS Technical info 640
 Обший каталог Yamawa 2016 - 2017
Обший каталог Yamawa 2016 - 2017 Краткое руководство Yamawa по каталогам
Краткое руководство Yamawa по каталогам Общий каталог Yamawa 2022 - 2023
Общий каталог Yamawa 2022 - 2023 Каталоги Yamawa твердосплавные метчики для закаленной стали
Каталоги Yamawa твердосплавные метчики для закаленной стали