Общий каталог Sumitomo 2018 - 2019 - страница 578
Навигация
- Pages 3-6_CS6_EN_web
- A 1-20 insert selection EN_web
- B 1-14 grades_EN_web
- C01-17 inserts intro pages_EN_web
- C18-56 negative inserts_EN_web
- C57-86 positive inserts_EN_web
- D 1-46 tool holders_EN_web
- E 1-24 boring bars_EN_web
- F 1-48 grooving_thread tools_EN_web
- G 1-54 milling cutters_EN_web
- H 1-48 insert type endmills_EN_web
- J 1-24 new endmills_EN_web
- J 25-50 endmills_EN_web
- K 1-46 Multi-Drills_EN_web
- K 47-76 Multi-Drills_EN_web
- L 1-28 cbn_pcd grades_EN_web
- M 1-34 cbn_pcd inserts_EN_web
- M 35-56 SHM tools_EN_web
- N1-24 technical guidance_EN_web
- P 1-8 spare parts_neu_EN_web
- P 9-22 index_notes_EN_web
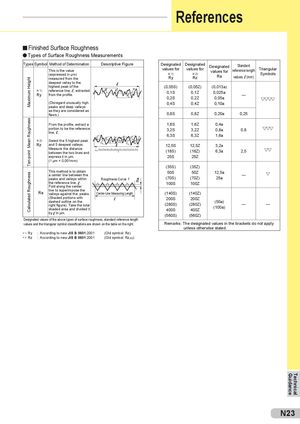
Maximum HeightMean RoughnessTen-pointCalculated Roughness Yp1 Yv1 Yp2 Yv2 Yp3 Yv3 Yp4 Yv4 Yp5 Yv5 References Finished Surface Roughness Types of Surface Roughness Measurements Types Symbol Method of Determination Descriptive FigureThis is the value(expressed in µm)measured from theDesignatedvalues forh 1)RyDesignatedvalues forh 2)RzDesignatedStandardvalues forreference lengthRavalues, l (mm)TriangularSymbols deepest valley to the highest peak of the (0,05S) (0,05Z) (0,013a) h 1) reference line, l, extractedRyfrom the profile. 0,1S0,2S 0,1Z 0,025a0,2Z0,05a— (Disregard unusually high 0,4S 0,4Z 0,10a peaks and deep valleys as they are considered as flaws.) 0,8S 0,8Z 0,20a 0,25 From the profile, extract a 1,6S 1,6Z 0,4a portion to be the referenceline, l. 3,2S 3,2Z 0,8a 0,8m6,3S6,3Z1,6a h 2) Select the 5 highest peak Rz and 5 deepest valleys. 12,5S 12,5Z 3,2a Measure the distancebetween the two lines and Rz= (Yp1+Yp2+Yp3+Yp4+Yp5)+(Yv1+Yv2+Yv3+Yv4+Yv5) 5 (18S) (18Z) 6,3a 2,5 express it in µm. 25S 25Z (1 µm = 0,001mm) (35S) (35Z) This method is to obtaina center line between thepeaks and valleys withinRoughness Curve f 50S 50Z 12,5a(70S)(70Z)25a— the reference line, l. 100S 100Z Fold along the center Ra line to superimpose thevalleys against thepeaks.Center-Line Measuring Length (140S) (140Z) (Shaded portions withdashed outline on theright figure). Take the totalshaded area and divided it 200S(280S)400S 200Z(280Z)400Z (50a)(100a) — — by l in µm. (560S) (560Z) Designated values of the above types of surface roughness, standard reference length values and the triangular symbol classifications are shown on the table on the right. Remarks: The designated values in the brackets do not apply unless otherwise stated. h 1) Ry : According to new JIS B 0601:2001 (Old symbol: Rz) h 2) Rz : According to new JIS B 0601:2001 (Old symbol: RzJIS) N23 Guidance Technical
 Общий каталог Sumitomo 2012
Общий каталог Sumitomo 2012 Каталог Sumitomo резьбонарезной инструмент
Каталог Sumitomo резьбонарезной инструмент Каталог Sumitomo пластины с режущей кромкой-моноалмаз Sumicristal
Каталог Sumitomo пластины с режущей кромкой-моноалмаз Sumicristal Каталог Sumitomo инструмент для обработки канавок
Каталог Sumitomo инструмент для обработки канавок Общий каталог Sumitomo 2019 - 2020
Общий каталог Sumitomo 2019 - 2020 Каталог Sumitomo запасные части
Каталог Sumitomo запасные части