Общий каталог Mitsubishi 2020 - 2021 - страница 1727
Навигация
 Каталог Mitsubishi Materials запасные части
Каталог Mitsubishi Materials запасные части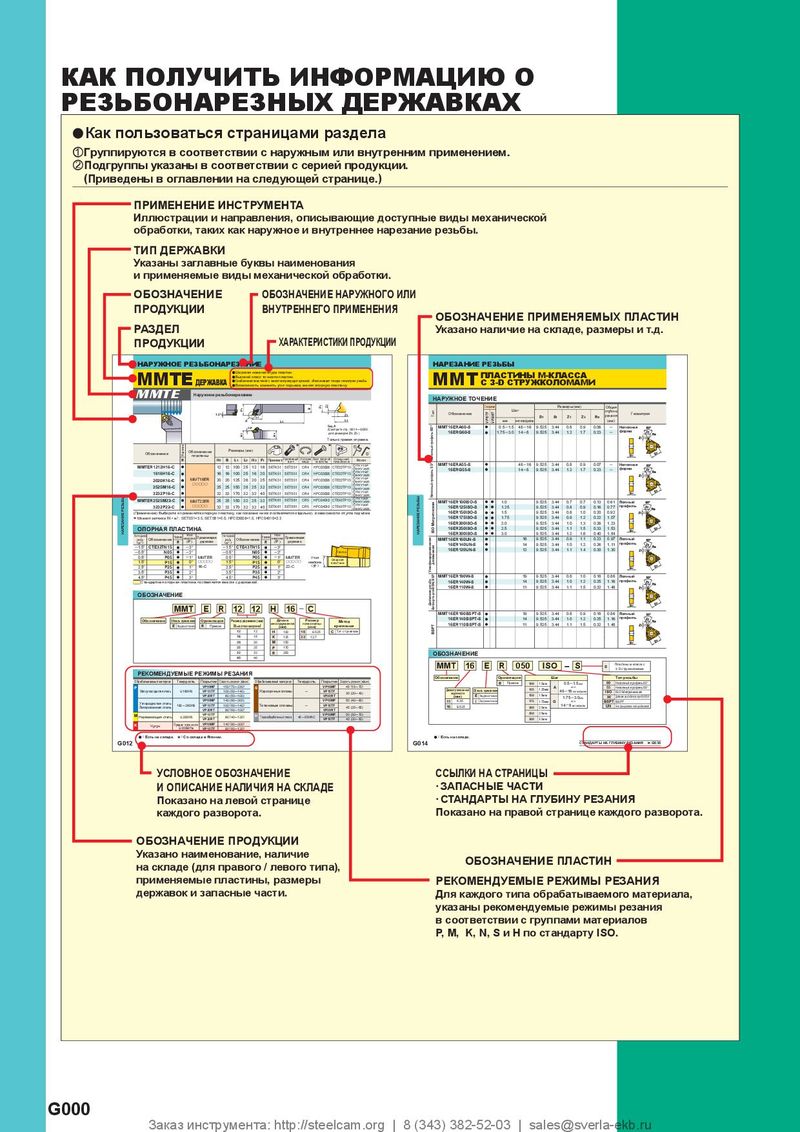 Каталог Mitsubishi Materials резьбонарезной инструмент
Каталог Mitsubishi Materials резьбонарезной инструмент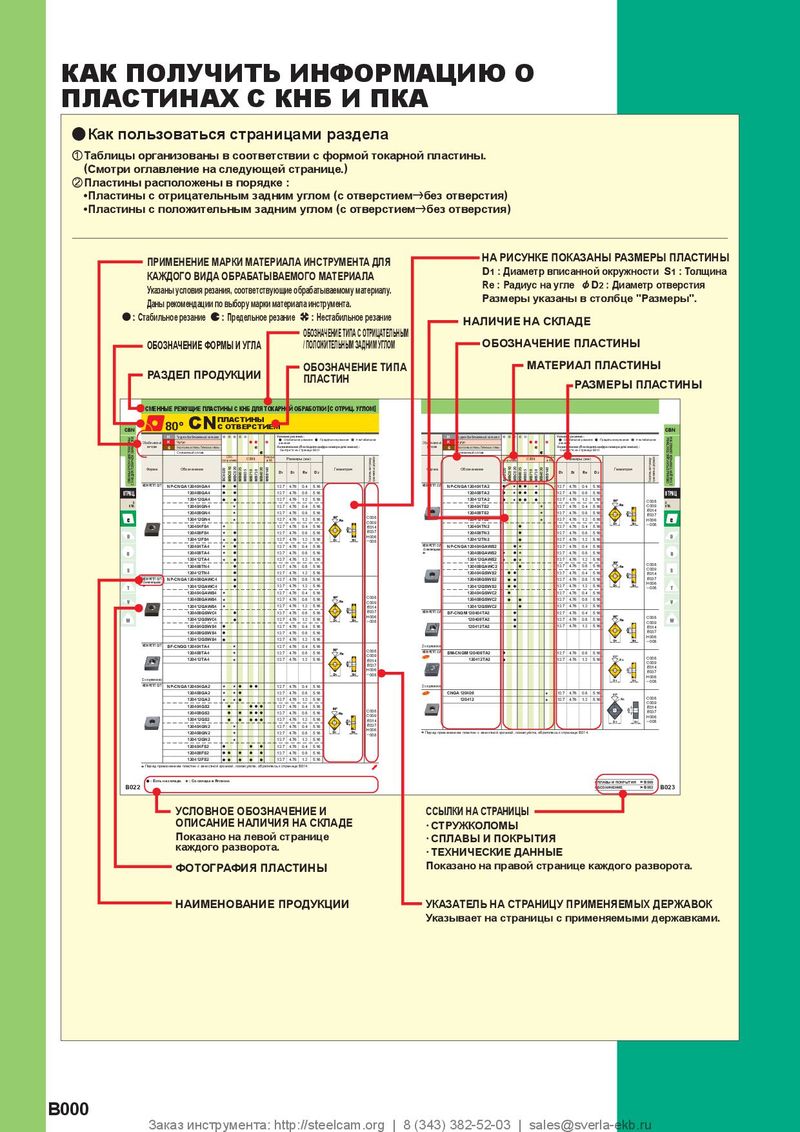 Каталог Mitsubishi Materials СНП с CBN и PCD для токарной обработки
Каталог Mitsubishi Materials СНП с CBN и PCD для токарной обработки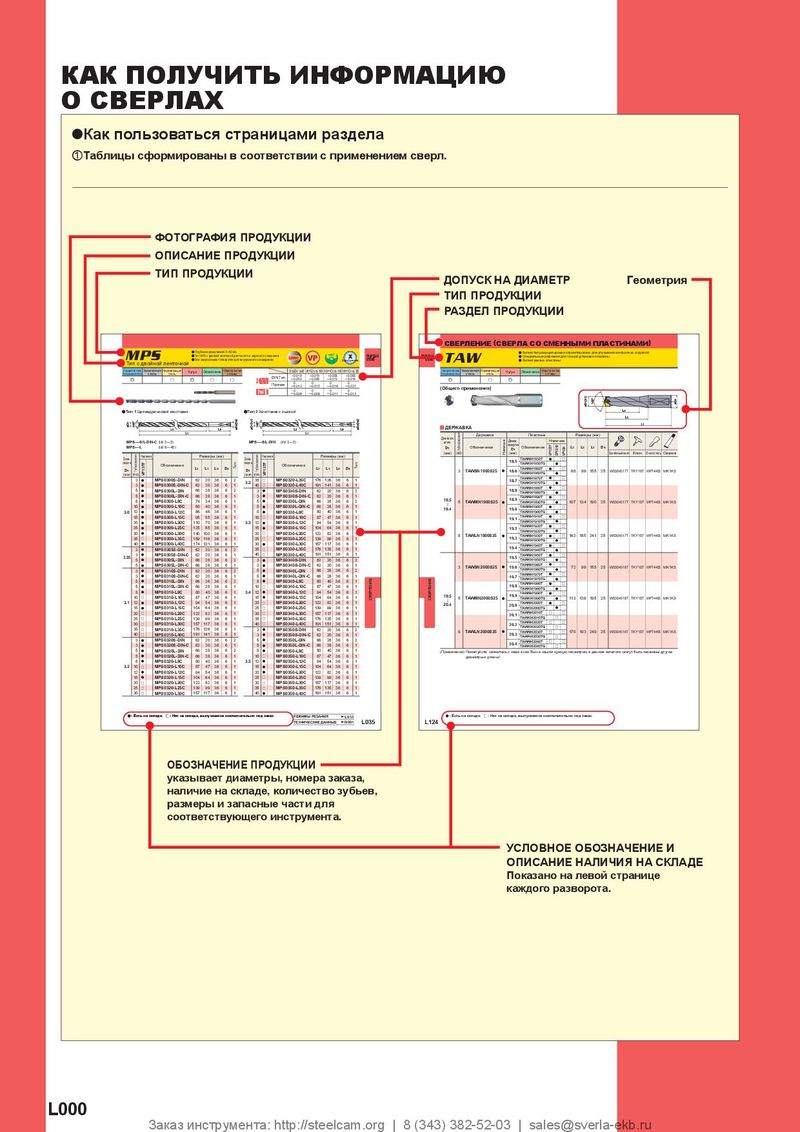 Каталог Mitsubishi Materials сверлильные инструменты
Каталог Mitsubishi Materials сверлильные инструменты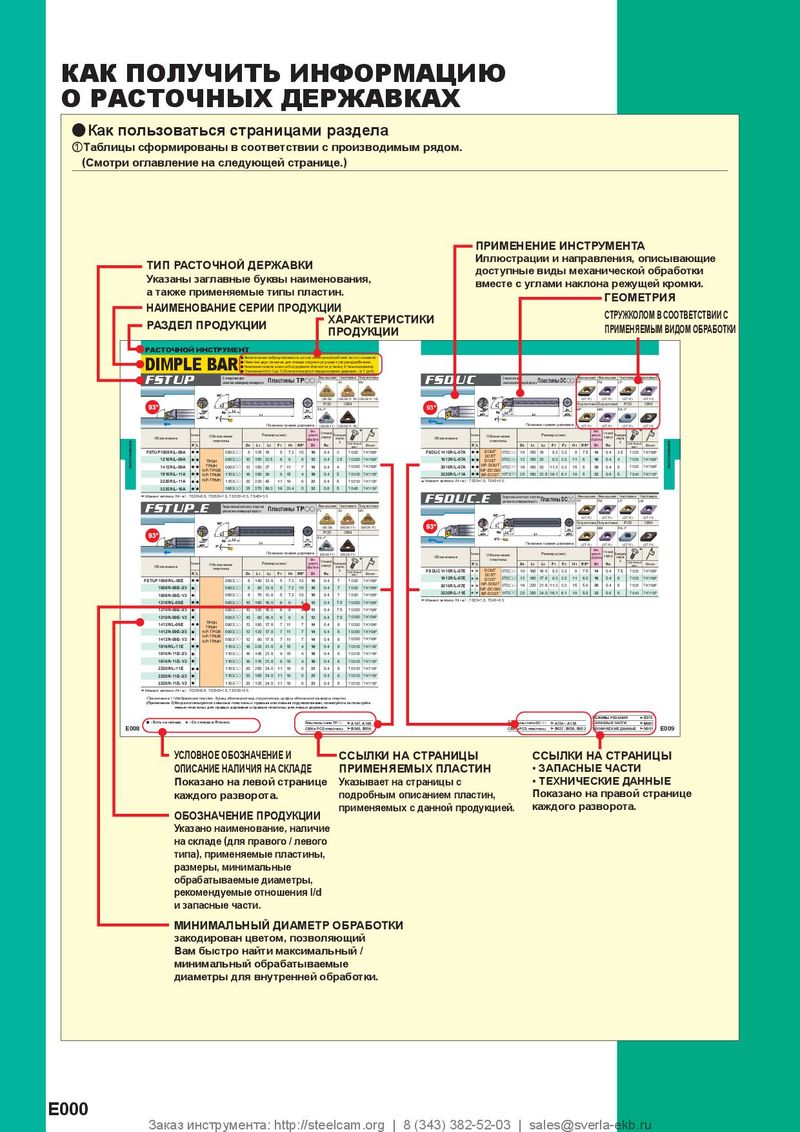 Каталог Mitsubishi Materials расточной инструмент
Каталог Mitsubishi Materials расточной инструмент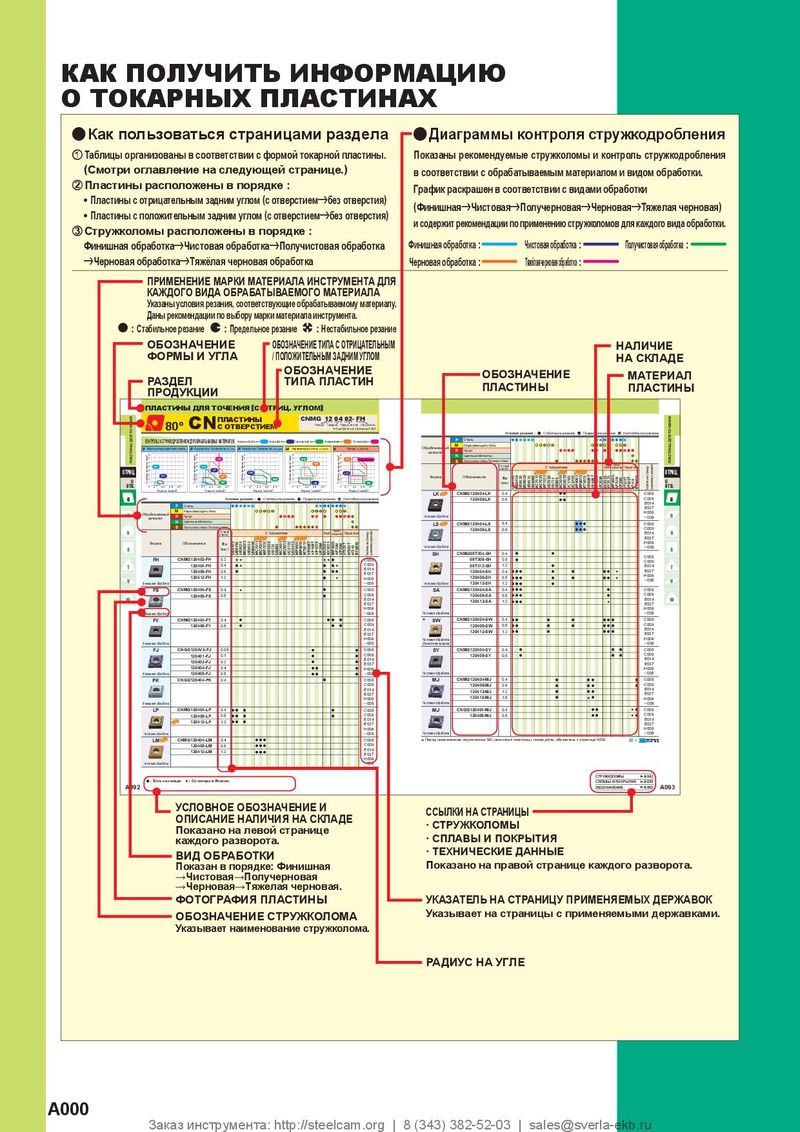 Каталог Mitsubishi Materials пластины для точения
Каталог Mitsubishi Materials пластины для точения 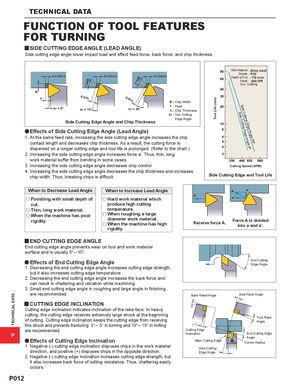
TECHNICAL DATA B 1.04B 1.15B Tool Life (min) Side CSiudtetinCguEttdinggeEAdnggeleA1n5g°le 0° TECHNICAL DATA FUNCTION OF TOOL FEATURES FOR TURNING y SIDE CUTTING EDGE ANGLE (LEAD ANGLE) Side cutting edge angle lower impact load and effect feed force, back force, and chip thickness. Work Material : Alloy steel f = Same f = Same f = Same Grade : P20Depth of Cut : .118 inch Feed : .008 IPR Dry Cutting h 0.97h 0.87h B : Chip Width kr = 0° kr = 15° f : Feedkr = 30°h : Chip Thickness kr : Tool Cutting Edge Angle Side Cutting Edge Angle and Chip Thickness aEffects of Side Cutting Edge Angle (Lead Angle) 1. At the same feed rate, increasing the side cutting edge angle increases the chip contact length and decreases chip thickness. As a result, the cutting force is dispersed on a longer cutting edge and tool life is prolonged. (Refer to the chart.) 2. Increasing the side cutting edge angle increases force a'. Thus, thin, long work material suffer from bending in some cases. 3. Increasing the side cutting edge angle decreases chip control. Cutting Speed (SFM) 4. Increasing the side cutting edge angle decreases the chip thickness and increases chip width. Thus, breaking chips is difficult. Side Cutting Edge and Tool Life When to Decrease Lead Angle When to Increase Lead Angle A a' Au Finishing with small depth ofu Hard work material whicha cut. produce high cutting u Thin, long work material. temperature. u When the machine has poorrigidity. u When roughing a largediameter work material.u When the machine has highReceive force A. Force A is dividedinto a and a'. rigidity. y END CUTTING EDGE ANGLE End cutting edge angle prevents wear on tool and work material surface and is usually 5°― 15°. a Effects of End Cutting Edge Angle End CuttingEdge Angle 1. Decreasing the end cutting edge angle increases cutting edge strength, but it also increases cutting edge temperature. 2. Decreasing the end cutting edge angle increases the back force and can result in chattering and vibration while machining. 3. Small end cutting edge angle in roughing and large angle in finishing are recommended. Back Relief Angle Side Flank Angle y CUTTING EDGE INCLINATION Cutting edge inclination indicates inclination of the rake face. In heavy cutting, the cutting edge receives extremely large shock at the beginningof cutting. Cutting edge inclination keeps the cutting edge from receiving True RakeAngle this shock and prevents fracturing. 3°― 5° in turning and 10°― 15° in milling (–) are recommended. Cutting Edge P Inclination End Cutting EdgeAngle a Effects of Cutting Edge Inclination Main Cutting Edge Corner Radius 1. Negative (-) cutting edge inclination disposes chips in the work material Side Cutting direction, and positive (+) disposes chips in the opposite direction. Edge Angle 2. Negative (-) cutting edge inclination increases cutting edge strength, but it also increases back force of cutting resistance. Thus, chattering easily occurs. P012