Общий каталог Mitsubishi 2020 - 2021 - страница 1725
Навигация
 Каталог Mitsubishi Materials запасные части
Каталог Mitsubishi Materials запасные части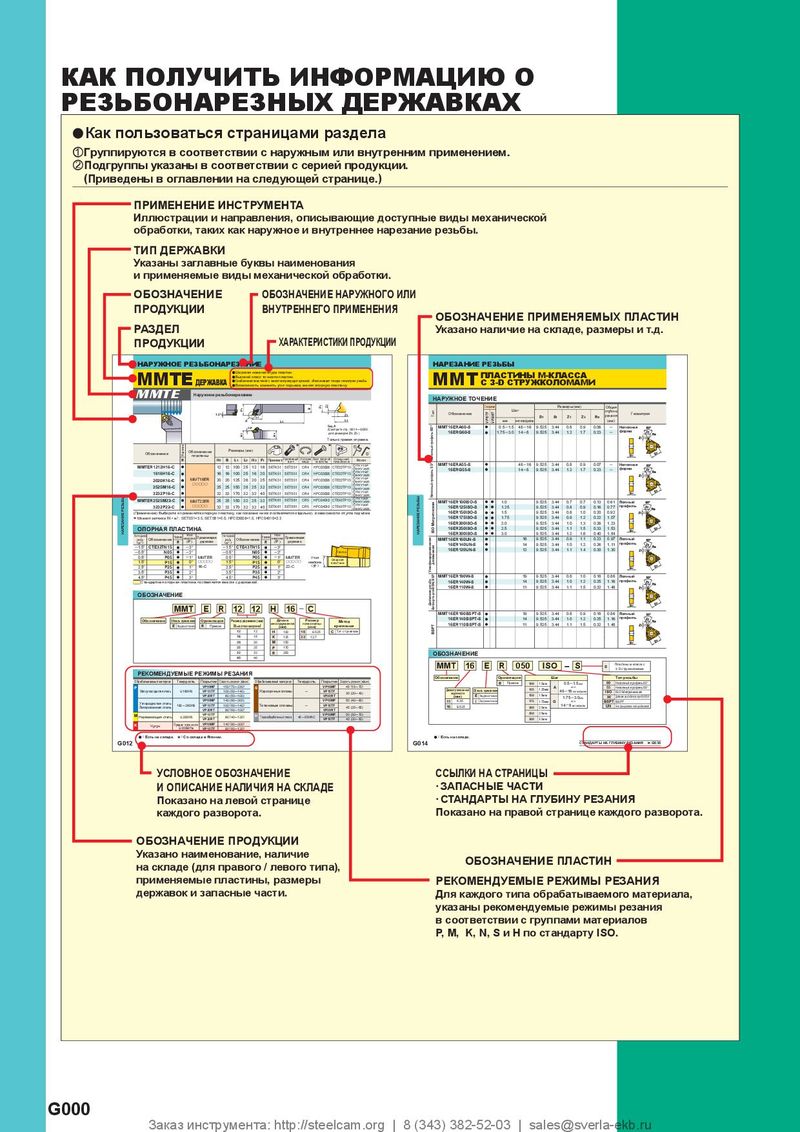 Каталог Mitsubishi Materials резьбонарезной инструмент
Каталог Mitsubishi Materials резьбонарезной инструмент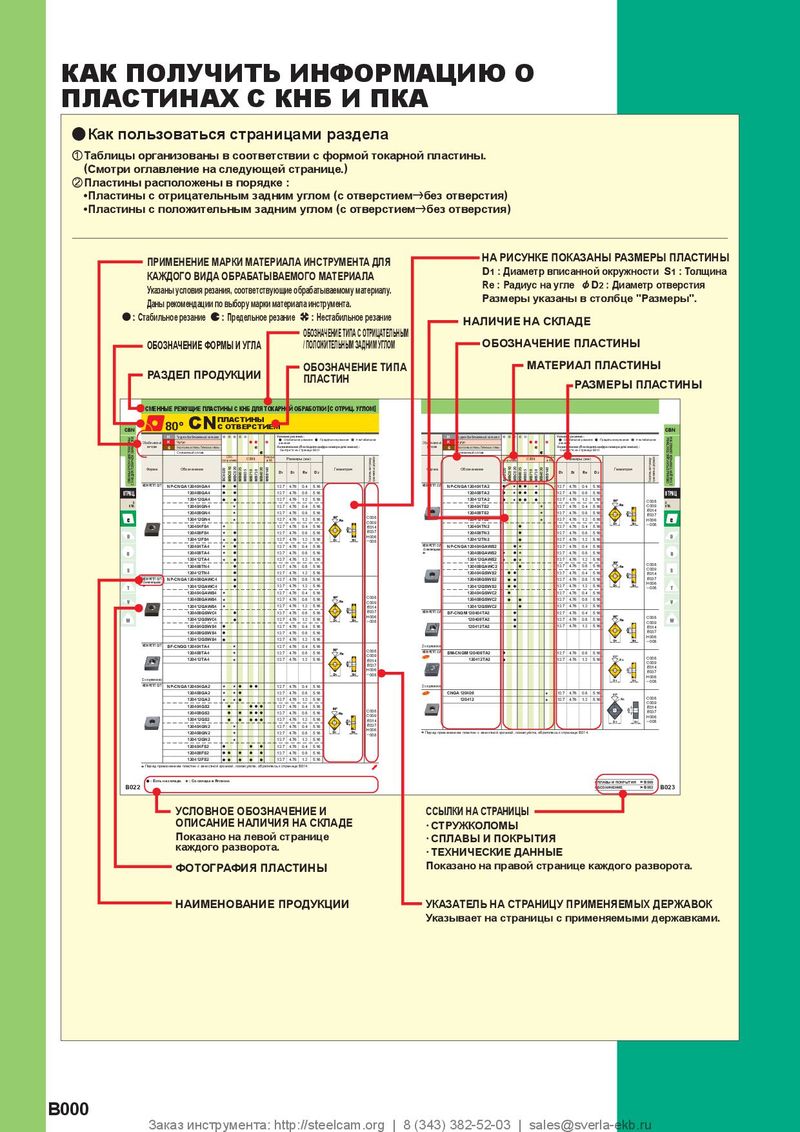 Каталог Mitsubishi Materials СНП с CBN и PCD для токарной обработки
Каталог Mitsubishi Materials СНП с CBN и PCD для токарной обработки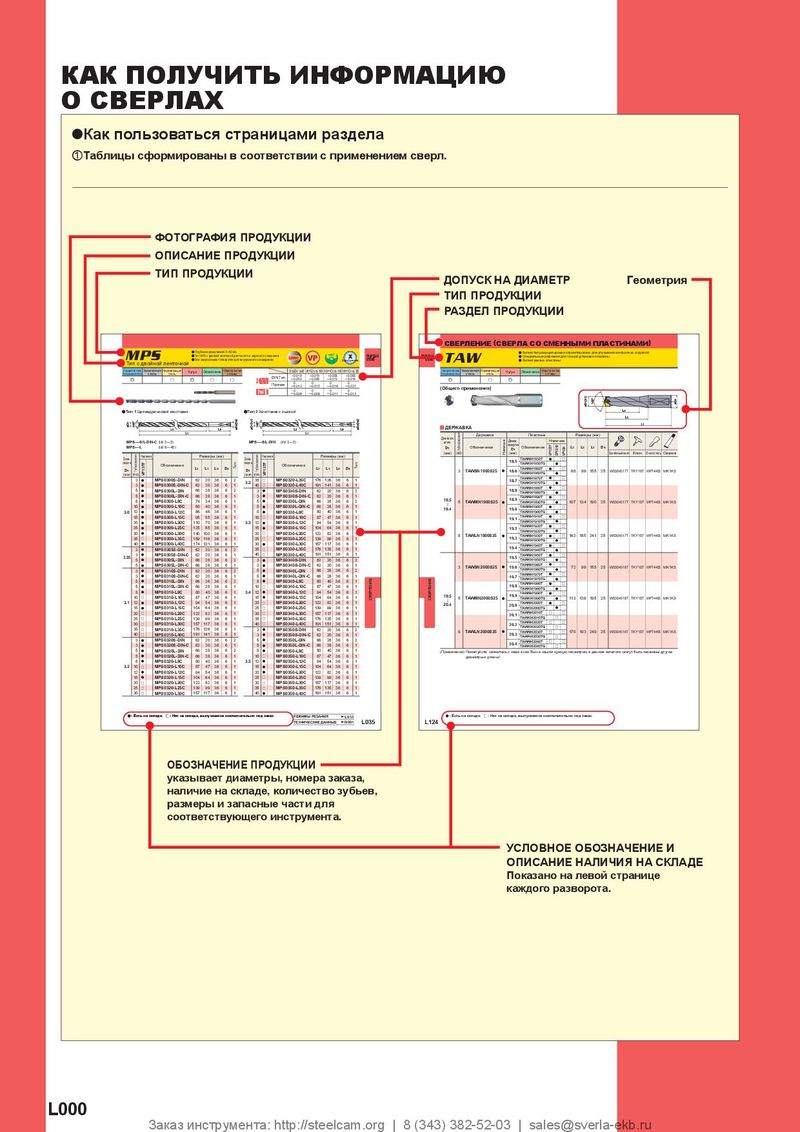 Каталог Mitsubishi Materials сверлильные инструменты
Каталог Mitsubishi Materials сверлильные инструменты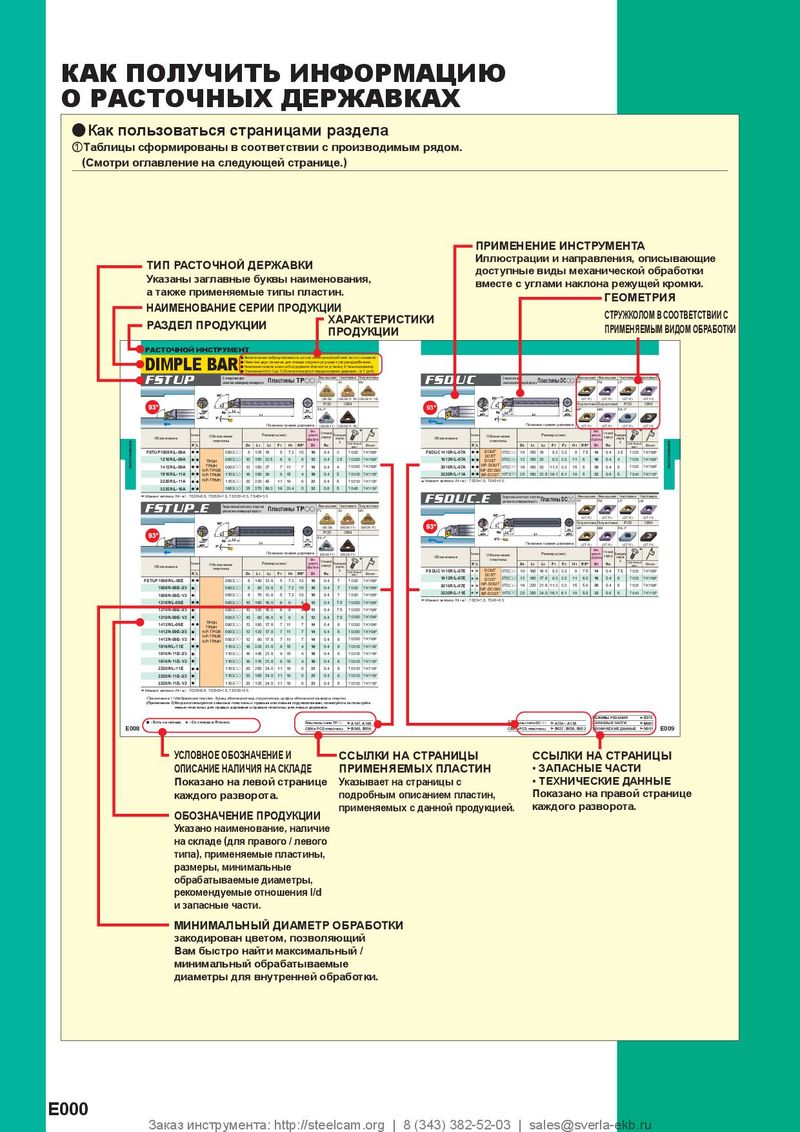 Каталог Mitsubishi Materials расточной инструмент
Каталог Mitsubishi Materials расточной инструмент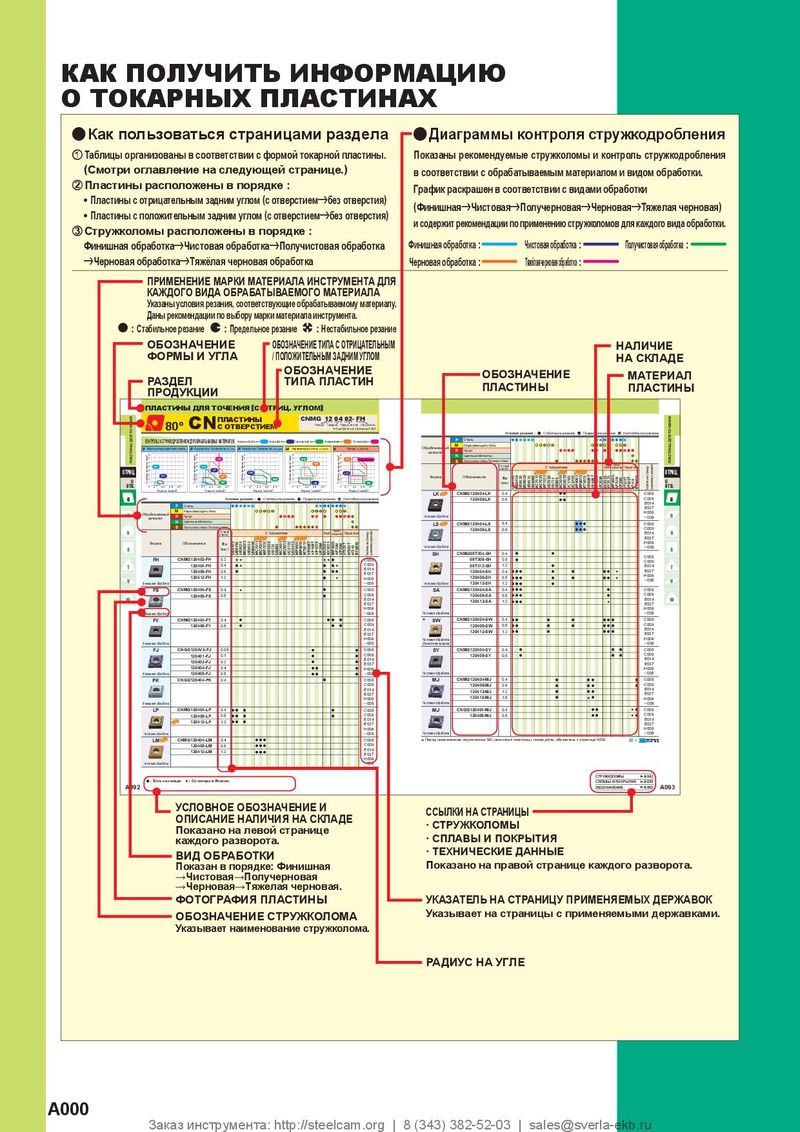 Каталог Mitsubishi Materials пластины для точения
Каталог Mitsubishi Materials пластины для точения 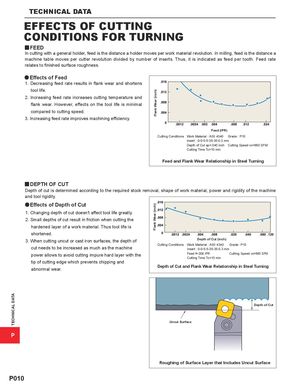
TECHNICAL DATA Flank Wear (inch)Flank Wear (inch) TECHNICAL DATA EFFECTS OF CUTTING CONDITIONS FOR TURNING y FEED In cutting with a general holder, feed is the distance a holder moves per work material revolution. In milling, feed is the distance a machine table moves per cutter revolution divided by number of inserts. Thus, it is indicated as feed per tooth. Feed rate relates to finished surface roughness. a Effects of Feed 1. Decreasing feed rate results in flank wear and shortens tool life. 2. Increasing feed rate increases cutting temperature and flank wear. However, effects on the tool life is minimal compared to cutting speed. 3. Increasing feed rate improves machining efficiency. Feed (IPR) Cutting Conditions Work Material : AISI 4340 Grade : P10 Insert : 0-0-5-5-35-35-0.3 mm Depth of Cut ap=.040 inch Cutting Speed vc=660 SFM Cutting Time Tc=10 min Feed and Flank Wear Relationship in Steel Turning y DEPTH OF CUT Depth of cut is determined according to the required stock removal, shape of work material, power and rigidity of the machine and tool rigidity. aEffects of Depth of Cut 1. Changing depth of cut doesn't affect tool life greatly. 2. Small depths of cut result in friction when cutting the hardened layer of a work material. Thus tool life is shortened. 3. When cutting uncut or cast iron surfaces, the depth of Depth of Cut (inch) Cutting Conditions Work Material : AISI 4340 Grade : P10 cut needs to be increased as much as the machine Insert : 0-0-5-5-35-35-0.3 mm power allows to avoid cutting impure hard layer with the Feed f=.008 IPR Cutting Speed vc=660 SFM Cutting Time Tc=10 min tip of cutting edge which prevents chipping and abnormal wear. Depth of Cut and Flank Wear Relationship in Steel Turning Depth of Cut Uncut Surface P Roughing of Surface Layer that Includes Uncut Surface P010