Каталог Guhring сверла со сменными пластинами - страница 30
Навигация
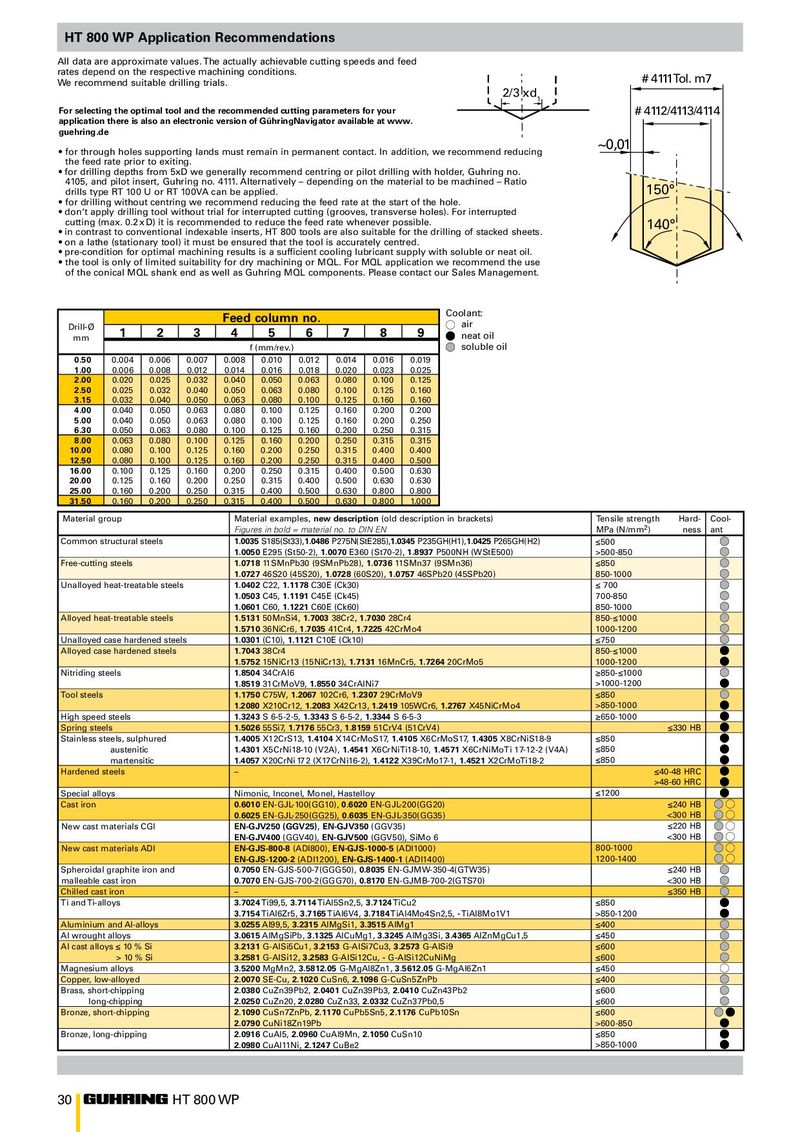
HT 800 WP Application Recommendations All data are approximate values. The actually achievable cutting speeds and feed rates depend on the respective machining conditions. We recommend suitable drilling trials. # 4111Tol. m7 2/3 xd 1 For selecting the optimal tool and the recommended cutting parameters for your # 4112/4113/4114 application there is also an electronic version of GühringNavigator available at www. guehring.de ~0,01 • for through holes supporting lands must remain in permanent contact. In addition, we recommend reducing the feed rate prior to exiting. • for drilling depths from 5xD we generally recommend centring or pilot drilling with holder, Guhring no. 4105, and pilot insert, Guhring no. 4111. Alternatively – depending on the material to be machined – Ratio drills type RT 100 U or RT 100VA can be applied. 150° • for drilling without centring we recommend reducing the feed rate at the start of the hole. • don‘t apply drilling tool without trial for interrupted cutting (grooves, transverse holes). For interrupted cutting (max. 0.2 x D) it is recommended to reduce the feed rate whenever possible. 140° • in contrast to conventional indexable inserts, HT 800 tools are also suitable for the drilling of stacked sheets. • on a lathe (stationary tool) it must be ensured that the tool is accurately centred. • pre-condition for optimal machining results is a sufficient cooling lubricant supply with soluble or neat oil. • the tool is only of limited suitability for dry machining or MQL. For MQL application we recommend the use of the conical MQL shank end as well as Guhring MQL components. Please contact our Sales Management. Coolant: Feed column no. Drill-Ø air mm 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 neat oil f (mm/rev.) soluble oil 0.50 0.004 0.006 0.007 0.008 0.010 0.012 0.014 0.016 0.019 1.00 0.006 0.008 0.012 0.014 0.016 0.018 0.020 0.023 0.025 2.00 0.020 0.025 0.032 0.040 0.050 0.063 0.080 0.100 0.125 2.50 0.025 0.032 0.040 0.050 0.063 0.080 0.100 0.125 0.160 3.15 0.032 0.040 0.050 0.063 0.080 0.100 0.125 0.160 0.160 4.00 0.040 0.050 0.063 0.080 0.100 0.125 0.160 0.200 0.200 5.00 0.040 0.050 0.063 0.080 0.100 0.125 0.160 0.200 0.250 6.30 0.050 0.063 0.080 0.100 0.125 0.160 0.200 0.250 0.315 8.00 0.063 0.080 0.100 0.125 0.160 0.200 0.250 0.315 0.315 10.00 0.080 0.100 0.125 0.160 0.200 0.250 0.315 0.400 0.400 12.50 0.080 0.100 0.125 0.160 0.200 0.250 0.315 0.400 0.500 16.00 0.100 0.125 0.160 0.200 0.250 0.315 0.400 0.500 0.630 20.00 0.125 0.160 0.200 0.250 0.315 0.400 0.500 0.630 0.630 25.00 0.160 0.200 0.250 0.315 0.400 0.500 0.630 0.800 0.800 31.50 0.160 0.200 0.250 0.315 0.400 0.500 0.630 0.800 1.000 Material group Material examples, new description (old description in brackets) Tensile strength Hard- Cool- Figures in bold = material no. to DIN EN MPa (N/mm 2 ) ness ant Common structural steels 1.0035 S185(St33),1.0486 P275N(StE285),1.0345 P235GH(H1),1.0425 P265GH(H2) ≤500 1.0050 E295 (St50-2), 1.0070 E360 (St70-2), 1.8937 P500NH (WStE500) >500-850 Free-cutting steels 1.0718 11SMnPb30 (9SMnPb28), 1.0736 11SMn37 (9SMn36) ≤850 1.0727 46S20 (45S20), 1.0728 (60S20), 1.0757 46SPb20 (45SPb20) 850-1000 Unalloyed heat-treatable steels 1.0402 C22, 1.1178 C30E (Ck30) ≤ 700 1.0503 C45, 1.1191 C45E (Ck45) 700-850 1.0601 C60, 1.1221 C60E (Ck60) 850-1000 Alloyed heat-treatable steels 1.5131 50MnSi4, 1.7003 38Cr2, 1.7030 28Cr4 850-≤1000 1.5710 36NiCr6, 1.7035 41Cr4, 1.7225 42CrMo4 1000-1200 Unalloyed case hardened steels 1.0301 (C10), 1.1121 C10E (Ck10) ≤750 Alloyed case hardened steels 1.7043 38Cr4 850-≤1000 1.5752 15NiCr13 (15NiCr13), 1.7131 16MnCr5, 1.7264 20CrMo5 1000-1200 Nitriding steels 1.8504 34CrAl6 ≥850-≤1000 1.8519 31CrMoV9, 1.8550 34CrAlNi7 >1000-1200 Tool steels 1.1750 C75W, 1.2067 102Cr6, 1.2307 29CrMoV9 ≤850 1.2080 X210Cr12, 1.2083 X42Cr13, 1.2419 105WCr6, 1.2767 X45NiCrMo4 >850-1000 High speed steels 1.3243 S 6-5-2-5, 1.3343 S 6-5-2, 1.3344 S 6-5-3 ≥650-1000 Spring steels 1.5026 55Si7, 1.7176 55Cr3, 1.8159 51CrV4 (51CrV4) ≤330 HB Stainless steels, sulphured 1.4005 X12CrS13, 1.4104 X14CrMoS17, 1.4105 X6CrMoS17, 1.4305 X8CrNiS18-9 ≤850 austenitic 1.4301 X5CrNi18-10 (V2A), 1.4541 X6CrNiTi18-10, 1.4571 X6CrNiMoTi 17-12-2 (V4A) ≤850 martensitic 1.4057 X20CrNi 17 2 (X17CrNi16-2), 1.4122 X39CrMo17-1, 1.4521 X2CrMoTi18-2 ≤850 Hardened steels – ≤40-48 HRC >48-60 HRC Special alloys Nimonic, Inconel, Monel, Hastelloy ≤1200 Cast iron 0.6010 EN-GJL-100(GG10), 0.6020 EN-GJL-200(GG20) ≤240 HB 0.6025 EN-GJL-250(GG25), 0.6035 EN-GJL-350(GG35) <300 HB New cast materials CGI EN-GJV250 (GGV25), EN-GJV350 (GGV35) ≤220 HB EN-GJV400 (GGV40), EN-GJV500 (GGV50), SiMo 6 <300 HB New cast materials ADI EN-GJS-800-8 (ADI800), EN-GJS-1000-5 (ADI1000) 800-1000 EN-GJS-1200-2 (ADI1200), EN-GJS-1400-1 (ADI1400) 1200-1400 Spheroidal graphite iron and 0.7050 EN-GJS-500-7(GGG50), 0.8035 EN-GJMW-350-4(GTW35) ≤240 HB malleable cast iron 0.7070 EN-GJS-700-2(GGG70), 0.8170 EN-GJMB-700-2(GTS70) <300 HB Chilled cast iron – ≤350 HB Ti and Ti-alloys 3.7024 Ti99,5, 3.7114 TiAl5Sn2,5, 3.7124 TiCu2 ≤850 3.7154 TiAl6Zr5, 3.7165 TiAl6V4, 3.7184 TiAl4Mo4Sn2,5, - TiAl8Mo1V1 >850-1200 Aluminium and Al-alloys 3.0255 Al99,5, 3.2315 AlMgSi1, 3.3515 AlMg1 ≤400 Al wrought alloys 3.0615 AlMgSiPb, 3.1325 AlCuMg1, 3.3245 AlMg3Si, 3.4365 AlZnMgCu1,5 ≤450 Al cast alloys ≤ 10 % Si 3.2131 G-AlSi5Cu1, 3.2153 G-AlSi7Cu3, 3.2573 G-AlSi9 ≤600 > 10 % Si 3.2581 G-AlSi12, 3.2583 G-AlSi12Cu, - G-AlSi12CuNiMg ≤600 Magnesium alloys 3.5200 MgMn2, 3.5812.05 G-MgAl8Zn1, 3.5612.05 G-MgAl6Zn1 ≤450 Copper, low-alloyed 2.0070 SE-Cu, 2.1020 CuSn6, 2.1096 G-CuSn5ZnPb ≤400 Brass, short-chipping 2.0380 CuZn39Pb2, 2.0401 CuZn39Pb3, 2.0410 CuZn43Pb2 ≤600 long-chipping 2.0250 CuZn20, 2.0280 CuZn33, 2.0332 CuZn37Pb0,5 ≤600 Bronze, short-chipping 2.1090 CuSn7ZnPb, 2.1170 CuPb5Sn5, 2.1176 CuPb10Sn ≤600 2.0790 CuNi18Zn19Pb >600-850 Bronze, long-chipping 2.0916 CuAl5, 2.0960 CuAl9Mn, 2.1050 CuSn10 ≤850 2.0980 CuAl11Ni, 2.1247 CuBe2 >850-1000 30 HT 800 WP
 Каталог Guhring пластины PKD и CBN
Каталог Guhring пластины PKD и CBN Основной каталог Guhring 2011
Основной каталог Guhring 2011 Каталог Guhring резьбонарезной инструмент
Каталог Guhring резьбонарезной инструмент Каталог Guhring зенкеры и зенковки
Каталог Guhring зенкеры и зенковки Каталог Guhring резьбонарезной инструмент 2010
Каталог Guhring резьбонарезной инструмент 2010 Каталог Guhring высокопроизводительный инструмент по отличной цене SuperLine
Каталог Guhring высокопроизводительный инструмент по отличной цене SuperLine